Groundwater
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Service types
Topics
-
This web service provides access to groundwater raster products for the Upper Burdekin region, including: inferred relative groundwater recharge potential derived from weightings assigned to qualitative estimates of relative permeability based on mapped soil type and surface geology; Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) used to map vegetation with potential access to groundwater in the basalt provinces, and; base surfaces of basalt inferred from sparse available data.
-
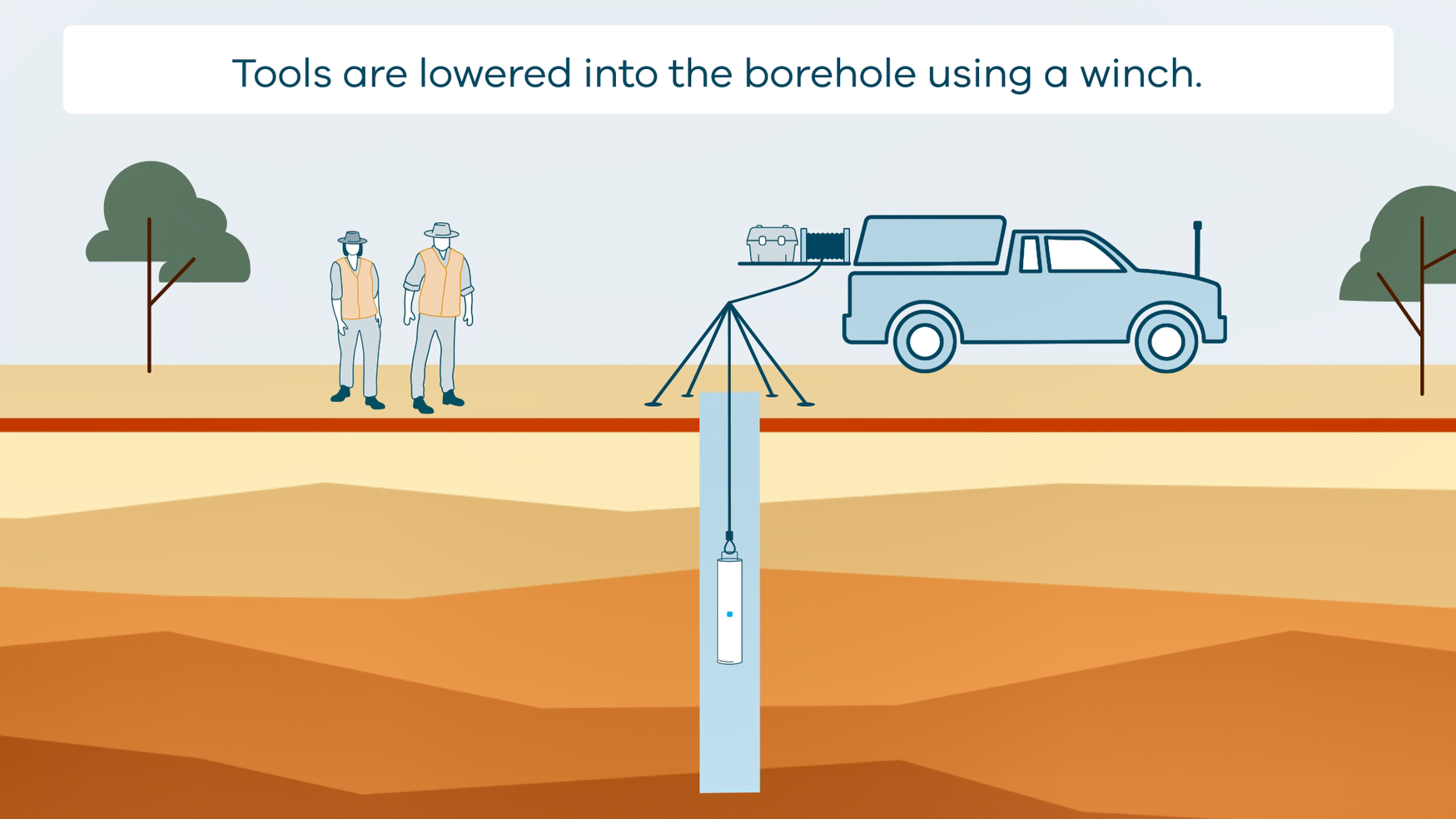
This animation shows how borehole geophysical surveys are conducted. It is part of a series of Field Activity Technique Engagement Animations. The target audience are the communities that are impacted by GA's data acquisition activities. There is no sound or voice over. The 2D animation includes a simplified view of what borehole geophysics equipment looks like, what the equipment measures and how scientists use the data.
-
This technical report details the methods and results the drilling programs of the Upper Burdekin Groundwater Project conducted as part of Exploring for the Future (EFTF)—an eight year, $225 million Australian Government funded geoscience data and information acquisition program focused on better understanding the potential mineral, energy and groundwater resources across Australia. This report was written by Queensland Government collaborators in the Department of Environment and Science, and is published here as supplied to Geoscience Australia at the conclusion of the project. The drilling program itself was conducted by the Department of Environment and Science as part of the Upper Burdekin Groundwater Project. A total of 17 holes were drilled in 2017-18 at 13 sites with a total combined depth of 943.2 metres. These comprise selected locations across both the Nulla Basalt Province and McBride Basalt Province. A network of 15 monitoring bores were constructed with two test holes backfilled and decommissioned.
-
The Western Davenport region has been identified as an area of interest for future agricultural development. However, realisation of this potential depends on access to a reliable supply of groundwater, underpinned by rigorous geological and groundwater information. A three-dimensional stratigraphic model has been created for the Western Davenport area of the Southern Stuart Corridor project under the Exploring for the Future program. Our interpretation integrates airborne electromagnetic data with historical drillhole and outcrop data to improve geological and hydrogeological understanding. Results show that stratigraphies of the Wiso and Georgina basins are equivalent and laterally continuous in this area. This enables a more complete hydrostratigraphy to be defined and underpins improved hydrogeological conceptualisation. New hydrochemical data support the conceptual model that the aquifers of the Wiso and Georgina basins are interconnected at a regional scale. The initial assessment of water quality indicates that groundwater may support further agricultural development. Analysis of new water chemistry data has improved understanding of groundwater processes and potential areas of recharge. This work will inform management decisions to enhance the economic and social opportunities in the Western Davenport area, while protecting the environmental and cultural value of water resources. <b>Citation:</b> Northey, J.E., Clark, A.D., Smith, M.L. and Hostetler, S., 2020. Delineation of geology and groundwater resources in a frontier region: Western Davenport, Northern Territory. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
The Exploring for the Future Project Areas web service depicts the spatial extents of project work undertaken as part of Geoscience Australia's $100.5 million initiative dedicated to boosting investment in resource exploration in Australia. Each project area extent has been generated by aggregating all project work sites into an envelope polygon. An indicative spend on each f the projects is also given.
-
We present a multifaceted hydrogeological investigation of the McBride and Nulla basalt provinces in the Upper Burdekin region, north Queensland. The project aims to better understand their key groundwater system processes to inform future development and water management decisions. This work, carried out as part of the Exploring for the Future Upper Burdekin Groundwater Project, has shown that basalt aquifers in each province are typically unconfined where monitored. Groundwater recharge is widespread but highly variable, largely occurring within the boundaries of the basalt provinces. Groundwater salinity based on electrical conductivity is <1000 μS/cm in the McBride Basalt Province (MBP) and up to 2000 μS/cm in the Nulla Basalt Province (NBP). Groundwater levels have been declining since 2011 (following major flooding in Queensland), showing that the study period covers a small fraction of a longer-functioning dynamic groundwater system. The basalt provinces contain distinct lava flows, and the degree of hydraulic connectivity between them is unclear. Despite similarities in their rock properties, the geometry of lava emplacement leads to different groundwater flow regimes within the two basalt provinces. Radial flow away from the central high elevations towards the edges is characteristic of the MBP, while regional flow from west to east dominates the NBP. Basalt aquifers in both provinces support a range of groundwater-dependent ecosystems, such as springs, some of which sustain flow in tributaries of the Burdekin River. Where streams intersect basalt aquifers, this also results in direct groundwater discharge. Springs and perennial tributaries, particularly emanating from the MBP, provide important inflows to the Burdekin River, especially in the dry season. This work has highlighted that management of MBP and NBP groundwater sources is crucial for maintaining a range of environmental assets in the region and for ensuring access for existing and future users. <b>Citation:</b> Ransley, T.R., Dixon-Jain, P., Cook, S.B., Lai, E.C.S., Kilgour, P., Wallace, L., Dunn, B., Hansen, J.W.L. and Herbert, G., 2020. Hydrogeology of the McBride and Nulla basalt provinces in the Upper Burdekin region, north Queensland. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
The Exploring for the Future Southern Stuart Corridor Groundwater Project undertook extensive multidisciplinary geoscientific investigations across four study areas and six Indigenous communities in central Australia to better understand and characterise groundwater resources. The project was developed to support improvements in water resilience for communities and future agricultural developments in the region. Geoscience Australia collected 9800 line kilometres of airborne electromagnetic data, drilled and installed 15 new monitoring bores, acquired 78 surface nuclear magnetic resonance soundings, recorded downhole geophysical data and groundwater level measurements from >50 bores, and completed hydrochemical analysis of 75 samples. Integration of these datasets provided insights into recharge areas and rates, and potential for managed aquifer recharge. The project also improved our understanding of the geological systems hosting groundwater and interconnections between systems. Potential new groundwater supplies, enhanced understanding of groundwater processes and improved geological models will assist water agencies to better manage groundwater resources across the region. <b>Citation:</b> Hostetler, S., Slatter, E., McPherson, A.A., Tan, K.P., McInnes, D. J., Wischusen, J.D.H. and Ellis, J.H., 2020. A multidisciplinary geoscientific approach to support water resilience in communities in Central Australia. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
Salinity of groundwater directly affects its suitability for different uses, including human consumption, stock water, agricultural use, and mineral or energy extraction. Traditionally, direct measurements of groundwater salinity at monitoring bores that intersect an aquifer have been used to map the spatial distribution of groundwater salinity. However, drilling is a logistically and economically challenging task, and we are usually left with a sparse set of measurements from which to infer groundwater salinity over large spatial extents. Airborne electromagnetic (AEM) sounding provides a solution to this problem. This is because AEM can be flown rapidly and cost-effectively over large swathes of land, and high subsurface bulk conductivities inferred from the AEM are well correlated with groundwater salinity in porous aquifers. We present here a methodology and case study from the Keep River Plains in the Northern Territory that provides information for land and watershed managers about the confidence with which salinity can be mapped over large areas using AEM. Extensive pore fluid sampling of the saturated zone, which lies beneath the watertable, enables this workflow to be used effectively. The results provided by our method can feed into decision making while accounting for uncertainty, enabling remote communities to manage their land and water resources effectively. <b>Citation:</b> Symington, N.,Ray, A., Harris-Pascal, C., Tan, K.P., Ley-Cooper, A.Y., and Brodie, R.C., 2020. Groundwater salinity estimation using borehole and AEM data: a framework for uncertainty analysis. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
Groundwater is an essential part of Darwin’s water supply mix, and is sourced from Howard East Borefield (HEB) and McMinns Borefield in the Koolpinyah Dolostone Aquifer (KDA), east of Darwin. Previous work suggested that electrical conductivity anomalies observed in airborne electromagnetic (AEM) data within 8 km of HEB may be caused by saline groundwater within the KDA that is separated from HEB by geological features that effectively compartmentalise the aquifer. Nevertheless, concerns grew that increased groundwater use may result in migration of saline groundwater towards HEB, which could compromise the groundwater resource. We collected hydrochemistry, including isotopes, time-series groundwater salinity and AEM data to better understand the complexities of the KDA. These data are presented here, along with a hydrodynamic analysis undertaken by the Northern Territory Department of Environment and Natural Resources, which shows that drawdown is occurring more rapidly from the NE of HEB and that dykes ~8 km NE of HEB act as barriers to groundwater flow. We show that groundwater sampled on the NE side of these dykes has a seawater composition. We use new AEM data to map the elevation of the top of unweathered dyke material and to characterise AEM conductors proximal to HEB. Our mapping reveals that the top of the unweathered portion of these dykes is commonly below sea level. We also show that AEM conductors proximal to HEB are more likely mineralised clays than saline groundwater within the aquifer. Drilling is required to confirm these results. Our findings contribute to building a robust conceptual understanding of the KDA and will inform future modelling of the groundwater system. <b>Citation:</b> Haiblen, A.M., Symington, N.J., Woltmann, M.J., Ray, A., Gow, L.J., Leplastrier, A. and McGrath, E.S.B., 2020. A multifaceted approach to investigating hydrogeological complexities in the Koolpinyah Dolostone Aquifer, Howard East, Northern Territory. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
Publicly available groundwater data have been compiled to provide a common information base to inform environmental, resource development and regulatory decisions in the Galilee Basin region. This data guide gives examples of how these data can be used. The data package included with this data guide captures existing knowledge of Galilee Basin aquifers and their properties, including salinity, water levels, resource size, potential aquifer yield and surface water - groundwater interactions. The methods used to derive these data for all Galilee Basin aquifers in the Galilee Basin region are outlined in the associated metadata files. These are described in groundwater conceptual models (Hostetler et al., 2023). The Galilee Basin includes 3 broadly defined aquifer intervals: from deepest to shallowest, these are the Joe Joe Group, Betts Creek beds and Clematis aquifers. Compiled data have been assigned to these intervals and used to characterise groundwater systems at the basin scale. The data were compiled for a point-in-time to inform decisions on potential resource developments in the Basin. The available historical groundwater data can be used to assess the potential effects on groundwater. The data can also be used for other purposes, such as exploring unallocated groundwater resource potential. Data to January 2022 were used for this compilation.