soil
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Scale
Topics
-
Data gathered in the field during the sample collection phase of the National Geochemical Survey of Australia (NGSA) has been used to compile the Preliminary Soil pH map of Australia. The map, which was completed in late 2009, offers a first-order estimate of where acid or alkaline soil conditions are likely to be expected. It provides fundamental datasets that can be used for mineral exploration and resource potential evaluation, environmental monitoring, landuse policy development, and geomedical studies into the health of humans, animals and plants.
-
The present report is a compilation of 531 geochemical maps that result from the National Geochemical Survey of Australia. These constitute the first continental-scale series of geochemical maps based on internally consistent, state-of-the-art data pertaining to the same sampling medium collected, prepared and analysed in a uniform and well documented manner and over a short time period (four years). Interpretations of the data and maps will be published separately. The geochemical maps can be used for better understanding the accumulation, mobility and significance of chemical elements in the near-surface environment of Australia. It is expected that they will provide a new, additional pre-competitive dataset for the energy and mineral resource exploration industry, which should help prioritise areas for further exploration investment and thus reduce risk. Further, it is also likely that some of the geochemical maps will find use in other disciplines related to natural resource management and environmental monitoring.
-
Spectral data from airborne and ground surveys enable mapping of the mineralogy and chemistry of soils in a semi-arid terrain of Northwest Queensland. The study site is a region of low relief, 20 km southeast of Duchess near Mount Isa. The airborne hyperspectral survey identified more than twenty surface components including vegetation, ferric oxide, ferrous iron, MgOH, and white mica. Field samples were analysed by spectrometer and X-ray diffraction to test surface units defined from the airborne data. The derived surface materials map is relevant to soil mapping and mineral exploration, and also provides insights into regolith development, sediment sources, and transport pathways, all key elements of landscape evolution.
-
We describe a model to predict soil-regolith thickness in a 128,000 ha study area in the central Mt Lofty Ranges in South Australia. The term soil-regolith includes the A, B, and C soil horizons to the lower boundary of the highly weathered bedrock zone (R horizon). The thickness of the soil-regolith has a major control on water holding capacity for plant growth and movement of water through the landscape, and as such, it is important in hydropedological modelling and in evaluating land suitability, e.g. for forestry and agriculture. Thickness estimates also have direct application in mineral exploration and seismic risk assessment. Geology and landscape evolution within the area is complex, reflecting the variable nature of bedrock materials, and the partial preservation of deeply weathered profiles as a consequence of weathering processes dating to the Cenozoic, or possibly older. These characteristics, together with strong climatic gradients across the area, make the study area an ideal location to understand the environmental and landscape evolution controls on weathering depth. The area also features weathered landscape analogues to many parts of southern Australia. We use a digital soil mapping piecewise linear decision tree approach to develop the model to predict soil-regolith thickness. This model is based on relationships established between 714 soil-regolith thickness measurements and 28 environmental covariates (e.g. rainfall, slope, gamma-ray spectrometry). The results establish a correlation R2 of 0.64, based on a 75:25% training:test data split. These results are encouraging, and are a significant advance over soil depth mapping by traditional soil-landscape mapping methods.
-
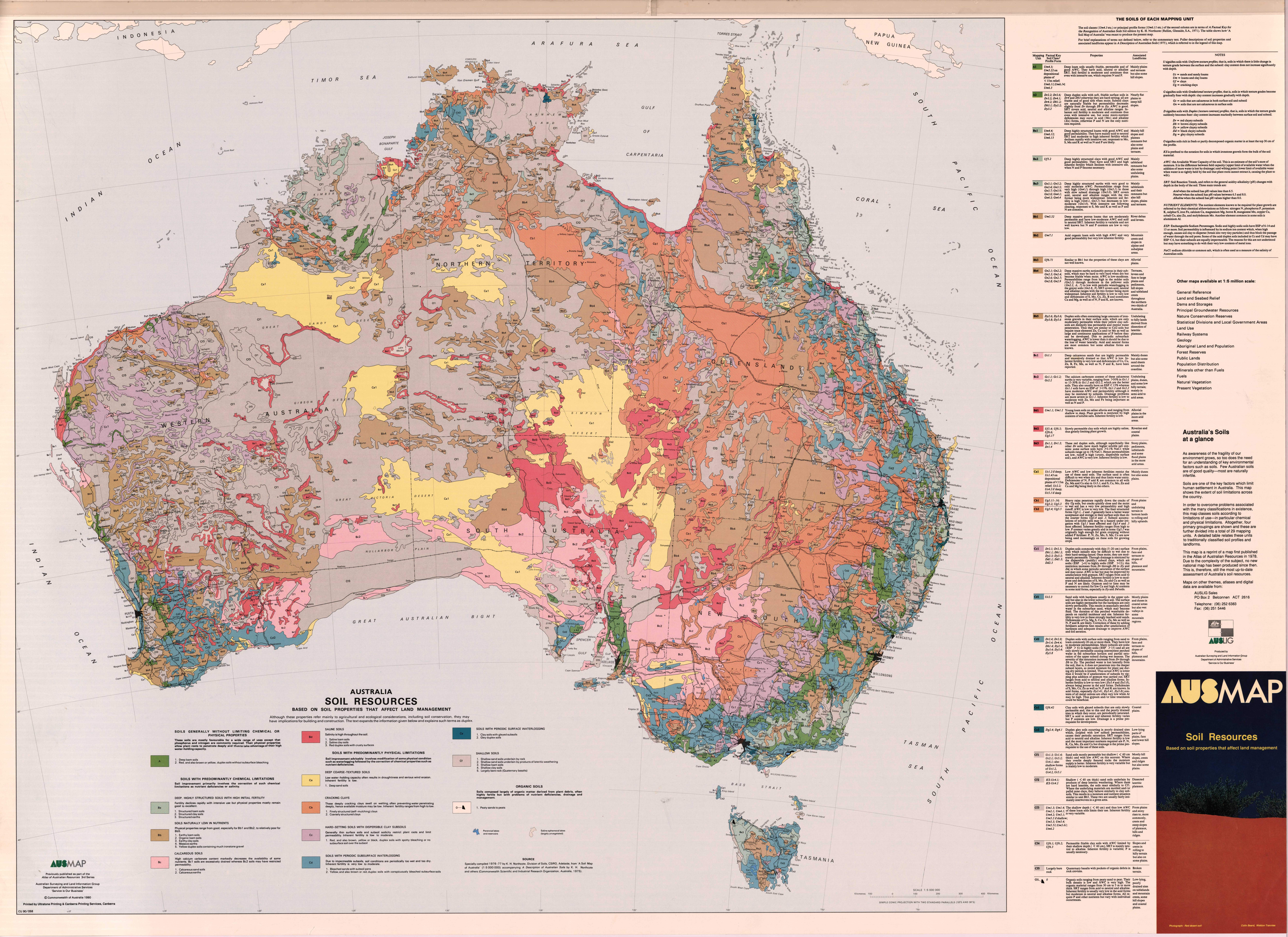
Soils are one of the key factors which limit human settlement in Australia. Few Australian soils are of good quality - most are naturally infertile. This map shows the extent of soil limitations across the country. In order to overcome problems associated with the many classifications in existence, this map classes soils according to limitations of use - in particular chemical and physical limitations. Altogether, four primary groupings are shown and these are further divided into a total of 29 mapping units. A detailed table relates these units to traditionally classified soil profiles and landforms. Product Specifications: Coverage: Australia Currency: 1976-77 Coordinates: Geographical Datum: AGD66 (GDA94 compliant at this scale) Projection: Simple Conic on two standard parallels 18S and 36S Medium: Paper, flat and folded copies
-
A weathering intensity index (WII) over the Australian continent has been developed at 100 m resolution using regression models based on airborne gamma-ray spectrometry imagery and the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) elevation data. Airborne gamma-ray spectrometry measures the concentration of three radioelements - potassium (K), thorium (Th) and uranium (U) at the Earth's surface. The total gamma-ray flux (dose) is also calculated based on the weighted additions of the three radioelements. Regolith accounts for over 85% of the Australian land area and has a major influence in determining the composition of surface materials and in controlling hydrological and geomorphological processes. The weathering intensity prediction is based on the integration of two regression models. The first uses relief over landscapes with low gamma-ray emissions and the second incorporates radioelement distributions and relief. The application of a stepwise forward multiple regression for the second model generated a weathering intensity index equation of: WII = 6.751 + -0.851*K + -1.319* Relief + 2.682 * Th/K + -2.590 * Dose. The WII has been developed for erosional landscapes but also has the potential to inform on deposition processes and materials. The WII correlates well with site based geochemical indices and existing regolith mapping. Interpretation of the WII from regional to local scales and its application in providing more reliable and spatially explicit information on regolith properties is described.
-
A shallow vertical CO2 injection test was conducted over a 21 day period at the Ginninderra Controlled Release Facility in May 2011. The objective of this test was to determine the extent of lateral CO2 dispersion, breakthrough times and permeability of the soil present at the Ginninderra site. The facility is located in Canberra on the CSIRO agricultural Ginninderra Experiment Station. A 2.15m deep, 15cm stainless steel screened, soil gas sampling well was installed at the site and this was used as the CO2 injection well. The CO2 flow rate was 1.6 L/min (STP). CO2 soil effluxes (respiration and seepage) were measured continuously using a LICOR LI-8100A Automated Soil CO2 Flux System equipped with 5 accumulation chambers spaced 1m apart in a radial pattern from the injection well. These measurements were supplemented with CO2 flux spot measurements using a WestSystems portable fluxmeter. Breakthrough at 1m from the injection point occurred within 6 hrs of injection, 32hrs at 2m and after almost 5 days at 3m. The average steady state CO2 efflux was 85 ?mol/m2/s at 1m, 15 ?mol/m2/s at 2m and 5.0 ?mol/m2/s at 3m. The average background CO2 soil respiration efflux was 1.1 - 0.6 ?mol/m2/s. Under windy conditions, higher soil CO2 efflux could be expected due to pressure pumping but this is contrary to the observed results. Prolonged windy periods led to a reduction in the CO2 efflux, up to 30% lower than the typical steady state value.
-
A new continental-scale geochemical atlas and dataset were officially released into the public domain at the end of June 2011. The National Geochemical Survey of Australia (NGSA) project, which started in 2007 under the Australian Government's Onshore Energy Security Program at Geoscience Australia, aimed at filling a huge knowledge gap relating to the geochemical composition of surface and near-surface materials in Australia. Better understanding the concentration levels and spatial distributions of chemical elements in the regolith has profound implications for energy and mineral exploration, as well as for natural resource management. In this world first project, a uniform regolith medium was sampled at an ultra-low density over nearly the entire continent, and subsamples from two depths and two grain-size fractions were analysed using up to three different (total, strong and weak) chemical digestions. This procedure yielded an internally consistent and comprehensive geochemical dataset for 68 chemical elements (plus additional bulk properties). From its inception, the emphasis of the project has been on quality control and documentation of procedures and results, and this has resulted in eight reports (including an atlas containing over 500 geochemical maps) and a large geochemical dataset representing the significant deliverables of this ambitious and innovative project. The NGSA project was carried out in collaboration with the geoscience agencies from every State and the Northern Territory under National Geoscience Agreements. .../...
-
Several quality control measures were taken during the project. These included: - Central provision of sampling equipment and sample bags to all field teams - Randomised sample identification scheme so that samples were presented to the laboratories in a sequence unrelated to the order in which they were collected (as much as practically feasible) - Prevention of contamination in the field and in the lab - Prevention of sample mix-up in the field and in the lab - Field duplicates: every 10th site, a field duplicate sample was collected to help quantify total (sampling + analytical) precision (not identified as such to the lab) - Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) TILL-1, TILL-2 (Natural Resources Canada) were run with every batch on GA's XRF & ICP-MS to help quantify analytical precision and bias - Laboratory duplicates (splits), internal project standards (MRIS, WRIS, ORIS, MRIS2, WRIS2), exchanged project standards (GEMAS-Ap, GEMAS-Gr from EuroGeoSurveys; SoNE-1 from United States Geological Survey), and international CRMs (TILL-1, TILL-3, LKSD-1, STSD-3 from Natural Resources Canada) were covertly inserted in the analytical suites for in-house and external analyses to help quantify analytical precision and bias (not identified as such to the lab) - Internal project standard (GRIS) for pH 1:5, EC 1:5 and grain size measurements (not identified as such to the lab) In addition to the above measures, the analytical labs applied their own QA/QC procedures, including running CRMs and/or internal standards, replicating digests and/or analysis, and analysis of blanks. The present report uses some of the above data to quantitatively assess the quality of the NGSA data, which allows a quality statement to be made about the NGSA data.
-
The use of airborne hyperspectral imagery for mapping soil surface mineralogy is examined for the semi-arid Tick Hill test site (20 km2) near Mount Isa in north-western Queensland. Mineral maps at 4.5 m pixel resolution include the abundances and physicochemistries (chemical composition and crystal disorder) of kaolin, illite-muscovite, and Al smectite (both montmorillonite and beidellite), as well as iron oxide, hydrated silica (opal), and soil/rock water (bound and unbound). Validation of these hyperspectral mineral maps involved field sampling (34 sites) and laboratory analyses (spectral reflectance and X-ray diffraction). The field spectral data were processed for their mineral information content the same way as the airborne HyMap data processing. The results showed significant spatial and statistical correlation. The mineral maps provide more detailed surface compositional information compared with the published soil and geology maps and other geoscience data (airborne radiometrics and digital elevation model). However, there is no apparent correlation between the published soil types (i.e. Ferrosols, Vertosols, and Tenosols) and the hyperspectral mineral maps (e.g. iron oxide-rich areas are not mapped as Ferrosols and smectite-rich areas are not mapped as Vertosols). This lack of correlation is interpreted to be related to the current lack of spatially comprehensive mineralogy for existing regional soil mapping. If correct, then this new, quantitative mineral mapping data has the potential to improve not just soil mapping but also soil and water catchment monitoring and modeling at local to regional scales. The challenges to achieving this outcome include gaining access to continental-scale hyperspectral data and models that link the surface mineralogy to subsurface soil characteristics/processes.
