Exploring for the Future
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Service types
Topics
-
The Layered Geology of Australia web map service is a seamless national coverage of Australia’s surface and subsurface geology. Geology concealed under younger cover units are mapped by effectively removing the overlying stratigraphy (Liu et al., 2015). This dataset is a layered product and comprises five chronostratigraphic time slices: Cenozoic, Mesozoic, Paleozoic, Neoproterozoic, and Pre-Neoproterozoic. As an example, the Mesozoic time slice (or layer) shows Mesozoic age geology that would be present if all Cenozoic units were removed. The Pre-Neoproterozoic time slice shows what would be visible if all Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic units were removed. The Cenozoic time slice layer for the national dataset was extracted from Raymond et al., 2012. Surface Geology of Australia, 1:1 000 000 scale, 2012 edition. Geoscience Australia, Canberra.
-
One of the aims of the Exploring for the Future program is to promote the discovery of new mineral deposits in undercover frontiers. Iron oxide–copper–gold mineral systems are a desirable candidate for undercover exploration, because of their potential to generate large deposits with extensive alteration footprints. This mineral potential assessment uses the mineral systems concept: developing mappable proxies of required theoretical criteria, combined to demonstrate where conditions favourable for mineral deposit formation are spatially coincident. This assessment uses a 2D geographical information system workflow to map the favourability of the key mineral system components. Two outputs were created: a comprehensive assessment, using all available spatial data; and a coverage assessment, which is constrained to data that have no reliance on outcrop. The results of these assessment outputs were validated with spatial statistics, demonstrating how the assessment can predict the presence of known ore deposits. Both assessment outputs present new areas of interest with prospectivity in under-explored regions of undercover northern Australia. The intended aims are already being realised, as this tool has aided area selection for pre-competitive stratigraphic drilling as part of the MinEx CRC National Drilling Initiative. <b>Citation:</b> Murr, J., Skirrow, R.G., Schofield, A., Goodwin, J., Coghlan, R., Highet, L., Doublier, M.P., Duan, J. and Czarnota, K., 2020. Tennant Creek – Mount Isa IOCG mineral potential assessment. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
The AusArray program aims to install small temporary passive seismic stations every 200 km across Australia. The seismic stations will passively measure small natural vibrations that travel through the Earth to help scientists understand the distribution and composition of rocks beneath the ground. Seismometers are sensitive instruments used to measure small natural vibrations that travel through the Earth caused by earthquakes, waves breaking on the shore and even wind. The data collected are analysed to create a three-dimensional model of the Earth’s subsurface. Passive seismic data can be used to model the Earth‘s structure, which is used to infer the geological history and assess the resource potential and natural hazards of the region.
-
This Record presents new Sensitive High Resolution Ion Micro Probe (SHRIMP) in situ monazite U–Pb geochronological results from the East Tennant area that were obtained in March 2022 as part of Geoscience Australia’s (GA) Exploring for the Future (EFTF) program. Three samples were targeted for monazite geochronology in order to constrain the timing of metamorphism and ductile deformation in the East Tennant area. Monazites in cordierite schist from the Alroy Formation in drill hole NDIBK01 (NDIBK01.300) yielded a weighted mean 207Pb/206Pb age of 1843.6 ± 6.1 Ma (95% confidence). Paragneiss from the Alroy Formation in drill hole NDIBK10 (NDIBK10.009) yielded monazites that returned a weighted mean 207Pb/206Pb crystallisation age of 1843.5 ± 5.1 Ma. Sparse monazites in sample NDIBK04.300, a garnet phyllite from drill hole NDIBK04, yielded a weighted mean 207Pb/206Pb crystallisation age of 1831 ± 28 Ma. These ages, from samples distributed throughout the East Tennant area, are interpreted to constrain the timing of an episode of low pressure, medium-grade metamorphism and coeval deformation.
-
The Officer Basin spanning South Australia and Western Australia is the focus of a regional stratigraphic study being undertaken as part of the Exploring for the Future (EFTF) program, an Australian Government initiative dedicated to increasing investment in resource exploration in Australia. Despite numerous demonstrated oil and gas shows, the Officer Basin remains a frontier basin for energy exploration with significant uncertainties due to data availability. Under the EFTF Officer-Musgrave Project, Geoscience Australia acquired new geomechanical rock property data from forty core samples in five legacy stratigraphic and petroleum exploration wells that intersected Paleozoic and Neoproterozoic aged intervals. These samples were subjected to unconfined compressive rock strength tests, Brazilian tensile strength tests and laboratory ultrasonic measurements. Petrophysical properties were also characterised via X-ray computerised tomography scanning, grain density and porosity-permeability analysis. Accurate characterisation of static geomechanical rock properties through laboratory testing is essential. In the modern exploration environment, these datasets are a precompetitive resource that can simplify investment decisions in prospective frontier regions such as the Officer Basin. Appeared in The APPEA Journal 62 S385-S391, 13 May 2022
-
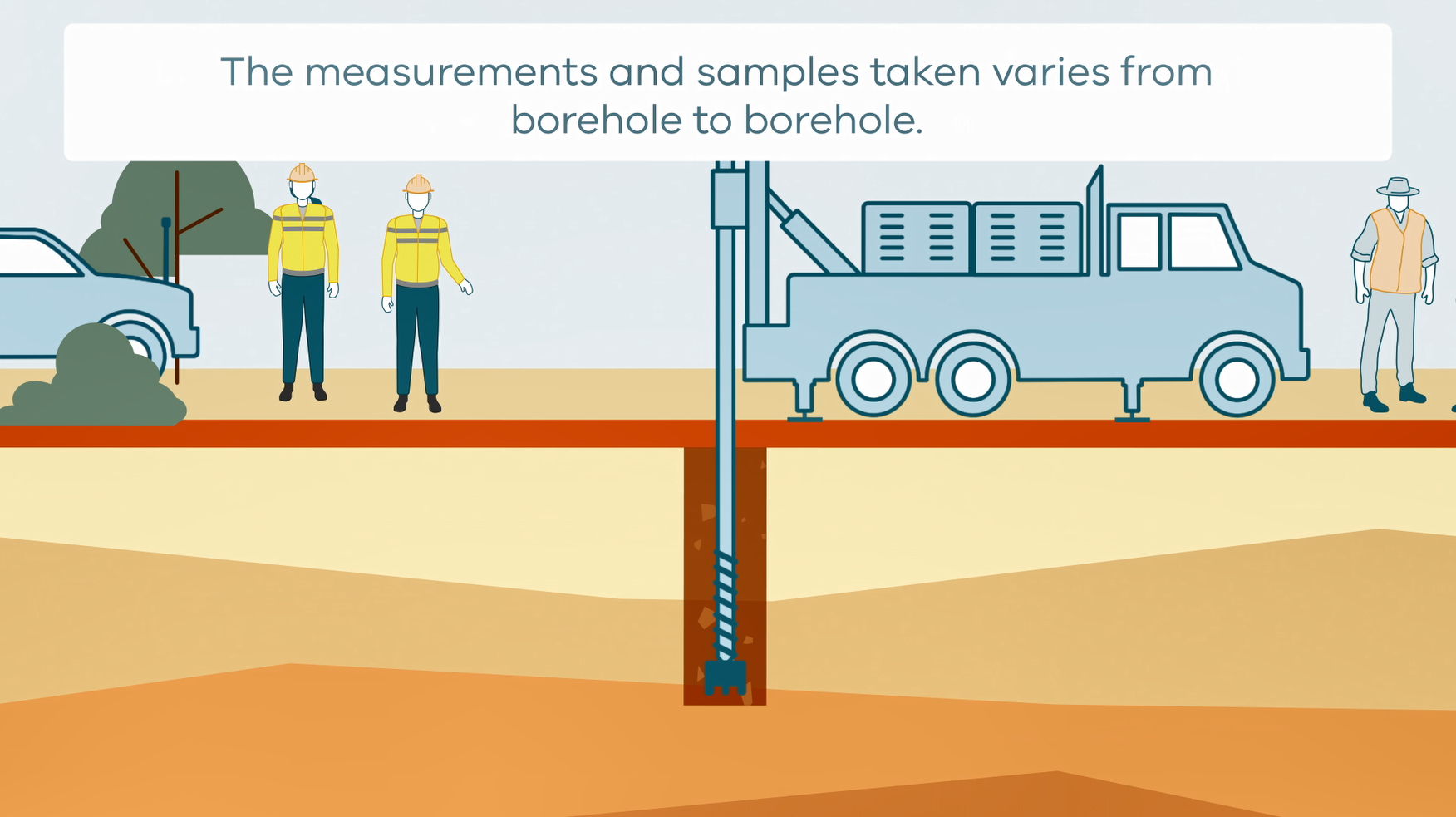
This animation shows how stratigraphic drilling is conducted. It is part of a series of Field Activity Technique Engagement Animations. The target audience are the communities that are impacted by GA's data acquisition activities. There is no sound or voice over. The 2D animation includes a simplified view of what stratigraphic drilling looks like, what measurements and samples are taken, and how scientists use the data.
-
This report presents key results of the Ti Tree Basin study completed as part of Exploring for the Future (EFTF)—an eight year, $225 million Australian Government funded geoscience data and information acquisition program focused on better understanding the potential mineral, energy and groundwater resources across Australia. As part of EFTF, Geoscience Australia undertook an assessment of available and new hydrochemical data collected in the Ti Tree Basin, Northern Territory. The basin is one of the four water control districts within the Southern Stuart Corridor Project area. Communities, irrigation farms and pastoral stations in the basin rely on groundwater, and extensive groundwater sampling and hydrochemical investigations have been undertaken over the past 50 years. An opportunity was recognised to collate and interpret the existing data, supplemented by new EFTF data, not only to add value to the understanding of groundwater processes in the basin itself but also to provide a useful knowledge base for other groundwater resources in the region that are poorly understood. This study largely relied on the available groundwater analysis data from the Northern Territory Department of Environment and Natural Resources database, supplemented by publicly available analyses from other sampling campaigns, including the EFTF, totaling 1913 groundwater samples across the district. The key findings of the study are: • The hydrochemistry data, particularly on salinity (total dissolved solids (TDS)), ion ratios (e.g. HCO3/Cl, Cl/(Cl+HCO3), Cl/(Cl+HCO3+SO4), Na/Cl) and radiocarbon (14C) could be used to map the three major recharge areas for the basin—the floodout of the Woodforde River to the west, the floodout of Allungra Creek in the basin centre, and the eastern basin margin. This is consistent with the current accepted interpretation that recharge is dominated by episodic run-on and infiltration in drainage floodout areas, driven by intense rainfall events that generate runoff in upland basement headwaters and ephemeral flows in basin creeks. There are no hydrochemical indicators of recharge in the vicinity of the channelised reaches of the basin creeks (i.e. both Woodforde River and Allungra Creek), located upstream of the floodouts. • From a groundwater resource perspective, the Allungra Creek floodout has broadly the best combination of low-salinity groundwater (median TDS = 740 mg/L) and bore yield statistics (median = 10 L/s). The Woodforde River floodout also has areas with high-yielding bores (>10 L/s) of fresh groundwater (<1000 mg/L), with the borehole distribution suggesting that the fresh groundwater resource is significantly more extensive to the west of the river than that previously mapped. The eastern basin margin generally has low-salinity groundwater (median TDS = 775 mg/L) but lower bore yields (median = 4.4 L/s). • There are differences in the recharge characteristics of the three floodout areas, due to differences in drainage catchments and floodout hydrogeology. The Woodforde River floodout has the most depleted stable isotopes, interpreted to be due to a higher rainfall/runoff threshold for recharge (>150 mm/month). It also has the largest isotopic range and the best δ18O-δ2H linear regression, suggesting the most influence of evaporation, such as a longer period of surface water ponding. In comparison, the stable isotope signature for Allungra Creek groundwaters suggests a lower rainfall/runoff threshold for recharge (>100 mm/month) and low evaporative influence, hence relatively rapid infiltration. This is also inferred to be the case for the low-salinity eastern basin margin groundwaters. For both Woodforde River and Allungra Creek, modern recharge is indicated by groundwaters with high radiocarbon activity (14C percent modern carbon (pMC) >70). For the eastern basin margin, radiocarbon activity is low to moderate (14C pMC 20–50). This is interpreted to reflect a longer travel time in the unsaturated zone. • In the floodout areas, the dominant hydrogeochemical process relating to the fresh groundwater is water–rock interactions. Groundwater tends to be the least evolved Ca(Mg)-HCO3 or transitional Na(K)-HCO3 water type, according to Chadha plots. Zones of prevalence of carbonate-gypsum dissolution or Na-silicate weathering could be mapped using indicators such as cation chloride ratio. Ion exchange is also a likely process in these fresh groundwaters, as inferred from chloro-alkaline indices. • Groundwater salinity is higher away from the floodout areas. This increased salinity is due to evapotranspirative concentration in addition to water–rock interactions, as inferred from ion ratios, including Cl/Br. Stable isotopes indicate that transpiration of groundwater by vegetation accessing the watertable, rather than direct evaporation, is the dominant process in these areas. This process is particularly evident in the Wilora Palaeochannel, the northern extension of the basin, which generally has the highest groundwater salinities (median TDS = 1575 mg/L), the lowest bore yields (median = 1.9 L/s) and the greatest prevalence of shallow watertables (<15 m). With higher salinities, groundwaters tend to be the evolved Ca(Mg)-Cl(SO4) and Na(K)-Cl(SO4) water types and potentially influenced by reverse ion exchange processes. • Mountain-front recharge has previously been proposed as an additional recharge mechanism, notably near the southern basin margin. Although sampling is limited in this area, hydrochemical indicators such as low HCO3/Cl, high Na/Cl and evolved Na(K)-Cl(SO4) water type suggests that active recharge is not significant. The watertable is deep along the southern basin margin (>50 m), so groundwater chemistry can be strongly influenced by processes during downward infiltration through a thick unsaturated zone. • Limited sampling of deeper bores (>80 m), potentially in the Hale Formation, generally have the characteristics of being more saline and lower yielding compared to bores in the shallow groundwater resource (particularly from 40 m to 80 m). However, there are deep bores with good yields of fresh groundwater; of 57 bores in the basin with interval depths exceeding 80 m, eight (14%) have the combination of yield >5 L/s and salinity <1000 mg/L. The deeper groundwaters are typically Ca(Mg)-Cl(SO4) and Na(K)-Cl(SO4) water types, with the latter, more evolved, water type dominating at depths >120 m. There are very few stable isotope analyses for the deeper groundwaters, but these are within the isotopic range for the shallow groundwaters in the same area, suggesting similarity in recharge processes and a degree of aquifer connectivity. Likewise, there are very few radiocarbon analyses for deeper groundwaters (depth >60 m), but these consistently show low 14C activity (pMC <40). The higher salinities, evolved water types and low 14C activity reflect longer residence times in the deeper groundwater system. The study highlighted that floodout recharge, involving episodic flow of basin creeks from headwater catchments, is the most dominant mechanism, rather than direct infiltration from large rainfall events. The study also identified that recharge characteristics, particularly the rainfall threshold for effective recharge and the role of evaporation, are not consistent across the floodout zones in the basin. This likely reflects differences in upland catchment size and geology, as well as floodout landform and hydrogeology. The study also highlighted the importance of groundwater-dependent vegetation in the basin, with dominance of transpiration of groundwater rather than direct evaporation. The groundwater hydrochemistry datasets and interpretation maps can support informed water management decisions within the basin. For example, improved understanding of the spatial and temporal distribution of recharge is not only needed for defining groundwater extraction limits but also used in strategies such as managed aquifer recharge. The EFTF work adds to the knowledge base and datasets that have developed over decades for the Ti Tree Basin, which are also valuable assets for broader understanding of groundwater resources in central Australia.
-
This Record documents the efforts of the Geological Survey of Victoria (GSV) and Geoscience Australia (GA) in compiling a geochronology (age) compilation for Victoria, describing both the dataset itself and the process by which it is incorporated into the continental-scale Isotopic Atlas of Australia. The Isotopic Atlas draws together age and isotopic data from across the country and provides visualisations and tools to enable non-experts to extract maximum value from these datasets. Data is added to the Isotopic Atlas in a staged approach with priorities determined by GA- and partner-driven focus regions and research questions. This dataset, which was primarily compiled by GSV and has been supplemented with data compiled by GA during the 2013–2017 Stavely Project, is a foundation for the second phase of the Exploring for the Future initiative over 2020–2024, particularly the Darling-Curnamona-Delamerian Project.
-
Crustal architecture places first-order controls on the distribution of mineral and energy resources. However, despite its importance, it is poorly constrained over much of northern Australia. Here, we present a full crustal interpretation of deep seismic reflection profile 18GA-KB1 that extends over 872 km from the Eo- to Mesoarchean Pilbara Craton to the Paleoproterozoic Aileron Province, transecting a range of stratigraphic and tectonic basement units, some of which are completely concealed by younger rocks. The seismic profile provides the first coherent image through this relatively poorly understood part of Australian geology and yields major new insights about the crustal architecture, geometry and definition of the different geological and seismic provinces and their boundaries. Key findings include the following: (1) The Pilbara Craton shows a three-component horizontal crustal layering, where the granite– greenstone East Pilbara Terrane is largely confined to the upper crust. (2) The Pilbara Craton has an extensive reworked margin, the Warrawagine Seismic Province, that thins towards the east, and underlies the western and central Rudall Province. (3) At the largest scale, the Rudall Province shows an approximately funnel-shaped geometry, with limited differences in seismic character between the various terranes. (4) The western Kidson Sub-basin is underlain by rocks of the Neoproterozoic Yeneena Basin and Rudall Province. (5) The central and eastern part of the Kidson Sub-basin rests on the coherent, relatively poorly structured Punmu Seismic Province, which is truncated by the steep, crustal-scale Lasseter Shear Zone, that marks the boundary to the Aileron Province to the east. <b>Citation:</b> Doublier, M.P., Johnson, S.P., Gessner, K., Howard, H., Chopping, R., Smithies, R.H., Martin, D.McB.,Kelsey, D.E., Haines, P.w., Hickman, A., Czarnota, K., Southby, C., Champion, D.C., Huston, D.L., Calvert, A.J., Kohanpour, F., Moro, P., Costelloe, R., Fomin, T. and Kennett, B.L.N., 2020. Basement architecture from the Pilbara Craton to the Aileron Province: new insights from deep seismic reflection line 18GA-KB1. In: Czarnota, K., Roach, I., Abbott, S., Haynes, M., Kositcin, N., Ray, A. and Slatter, E. (eds.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, 1–4.
-
The Exploring for the Future program is an initiative by the Australian Government dedicated to boosting investment in resource exploration in Australia. As part of the Exploring for the Future program, this study aims to improve our understanding of the petroleum resource potential of northern Australia. This data release presents new field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) of broad ion beam- polished samples (BIB-SEM) to visualise mineral and organic matter (OM) porosity on 15 Proterozoic aged shales. Samples were selected from the Velkerri and Barney Creek formations in the McArthur Basin and the Mullera Formation, Riversleigh Siltstone, Lawn Hill and Termite Range formations in the South Nicholson region. Qualitative maceral analysis of the 15 samples are described in addition to bitumen reflectance measurements. These samples were analysed at the Montanuniversität Leoben, Austria in June 2020. The results of this study can be used to improve our understanding of porosity, microstructures, seal capacity and hydrocarbon prospectivity of Proterozoic aged sedimentary basins in northern Australia.