2022
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Service types
Scale
Topics
-
Total magnetic intensity (TMI) data measures variations in the intensity of the Earth's magnetic field caused by the contrasting content of rock-forming minerals in the Earth crust. Magnetic anomalies can be either positive (field stronger than normal) or negative (field weaker) depending on the susceptibility of the rock. The data are processed via standard methods to ensure the response recorded is that due only to the rocks in the ground. The results produce datasets that can be interpreted to reveal the geological structure of the sub-surface. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose. These line dataset from the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021 survey were acquired in 2021 by the NSW Government, and consisted of line-kilometres of data at 200m line spacing and 60m terrain clearance.
-
This web service features Australian hydrogen projects that are actively in the investigation, construction, or operating phase, and that align with green hydrogen production methods as outlined in Australia's National Hydrogen Strategy. The purpose of this dataset is to provide a detailed snapshot of hydrogen activity across Australia, and includes location data, operator/organisation details, and descriptions for all hydrogen projects listed.
-
The Southeast Tasmania and Southern Macquarie Ridge Bathymetry dataset was acquired by the Australian Geological Survey Organisation (AGSO) (Geoscience Australia predecessor) during the AUSTREA-2 marine survey undertaken from 15 January - 9 February 2000 onboard the French Oceanographic and Geoscience Research Vessel N/O L'Atalante using a Simrad EM12D multibeam sonar system. The survey was completed as part of the work to map the foot-of-slope position to support definition of Australia's legal Continental Shelf under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. This dataset contains 120m-, 160m-, 250m-, 280m-, 300m-, 360m- and 440m-resolution 32-bit floating point GeoTIFF files of the bathymetry in the survey area, derived from the processed EM12D bathymetry data, using CARIS HIPS and SIPS software. This dataset is not to be used for navigational purposes.
-
The radiometric, or gamma-ray spectrometric method, measures the natural variations in the gamma-rays detected near the Earth's surface as the result of the natural radioactive decay of potassium (K), uranium (U) and thorium (Th). The data collected are processed via standard methods to ensure the response recorded is that due only to the rocks in the ground. The results produce datasets that can be interpreted to reveal the geological structure of the sub-surface. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose. This radiometric potassium grid has a cell size of 0.00039074 degrees (approximately 40m) and shows potassium element concentration of the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021 in units of percent (or %). The data used to produce this grid was acquired in 2021 by the NSW Government, and consisted of 53617 line-kilometres of data at 200m line spacing and 60m terrain clearance.
-
Total magnetic intensity (TMI) data measures variations in the intensity of the Earth's magnetic field caused by the contrasting content of rock-forming minerals in the Earth crust. Magnetic anomalies can be either positive (field stronger than normal) or negative (field weaker) depending on the susceptibility of the rock. The data are processed via standard methods to ensure the response recorded is that due only to the rocks in the ground. The results produce datasets that can be interpreted to reveal the geological structure of the sub-surface. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose. These line dataset from the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021 survey were acquired in 2021 by the NSW Government, and consisted of line-kilometres of data at 200m line spacing and 60m terrain clearance.
-
Total magnetic intensity (TMI) data measures variations in the intensity of the Earth's magnetic field caused by the contrasting content of rock-forming minerals in the Earth crust. Magnetic anomalies can be either positive (field stronger than normal) or negative (field weaker) depending on the susceptibility of the rock. The data are processed via standard methods to ensure the response recorded is that due only to the rocks in the ground. The results produce datasets that can be interpreted to reveal the geological structure of the sub-surface. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose. These line dataset from the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021 survey were acquired in 2021 by the NSW Government, and consisted of line-kilometres of data at 200m line spacing and 60m terrain clearance.
-
DEA Surface Reflectance OA (Sentinel-2B MSI) is part of a suite of Digital Earth Australia's (DEA) Surface Reflectance datasets that represent the vast archive of images captured by the US Geological Survey (USGS) Landsat and European Space Agency (ESA) Sentinel-2 satellite programs, which have been validated, calibrated, and adjusted for Australian conditions — ready for easy analysis. <b>Background:</b> This is a sub-product of Geoscience Australia Sentinel-2B MSI Analysis Ready Data Collection 3 - DEA Surface Reflectance (Sentinel-2B MSI). See the parent product for more information. The contextual information related to a dataset is just as valuable as the data itself. This information, also known as data provenance or data lineage, includes details such as the data’s origins, derivations, methodology and processes. It allows the data to be replicated and increases the reliability of derivative applications. Data that is well-labelled and rich in spectral, spatial and temporal attribution can allow users to investigate patterns through space and time. Users are able to gain a deeper understanding of the data environment, which could potentially pave the way for future forecasting and early warning systems. The surface reflectance data produced by NBART requires accurate and reliable data provenance. Attribution labels, such as the location of cloud and cloud shadow pixels, can be used to mask out these particular features from the surface reflectance analysis, or used as training data for machine learning algorithms. Additionally, the capacity to automatically exclude or include pre-identified pixels could assist with emerging multi-temporal and machine learning analysis techniques. <b>What this product offers:</b> This product contains a range of pixel-level observation attributes (OA) derived from satellite observation, providing rich data provenance: - null pixels - clear pixels - cloud pixels - cloud shadow pixels - snow pixels - water pixels - spectrally contiguous pixels - terrain shaded pixels It also features the following pixel-level information pertaining to satellite, solar and sensing geometries: - solar zenith - solar azimuth - satellite view - incident angle - exiting angle - azimuthal incident - azimuthal exiting - relative azimuth - timedelta
-
Digital Elevation data record the terrain height variations from the processed point- or line-located data recorded during a geophysical survey. This Cobar P5009 EXT 6 digital elevation model radar grid is elevation data for the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021. This survey was acquired under the project No. 5009 for the geological survey of NSW. The grid has a cell size of 0.00039074 degrees (approximately 40m). This grid contains the ground elevation relative to the geoid for the Cobar Magnetic and Radiometric Survey, 2021. It represents the vertical distance from a location on the Earth's surface to the geoid. The data are given in units of meters. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose.
-
The radiometric, or gamma-ray spectrometric method, measures the natural variations in the gamma-rays detected near the Earth's surface as the result of the natural radioactive decay of potassium (K), uranium (U) and thorium (Th). The data collected are processed via standard methods to ensure the response recorded is that due only to the rocks in the ground. The results produce datasets that can be interpreted to reveal the geological structure of the sub-surface. The processed data is checked for quality by GA geophysicists to ensure that the final data released by GA are fit-for-purpose. This Cobar magnetic and radiometric survey, NSW, 2021 (P5009), Extension 1, radiometric line data were acquired in 2021 by the NSW Government, and consisted of line-kilometres of data at 200m line spacing and 60m terrain clearance.
-
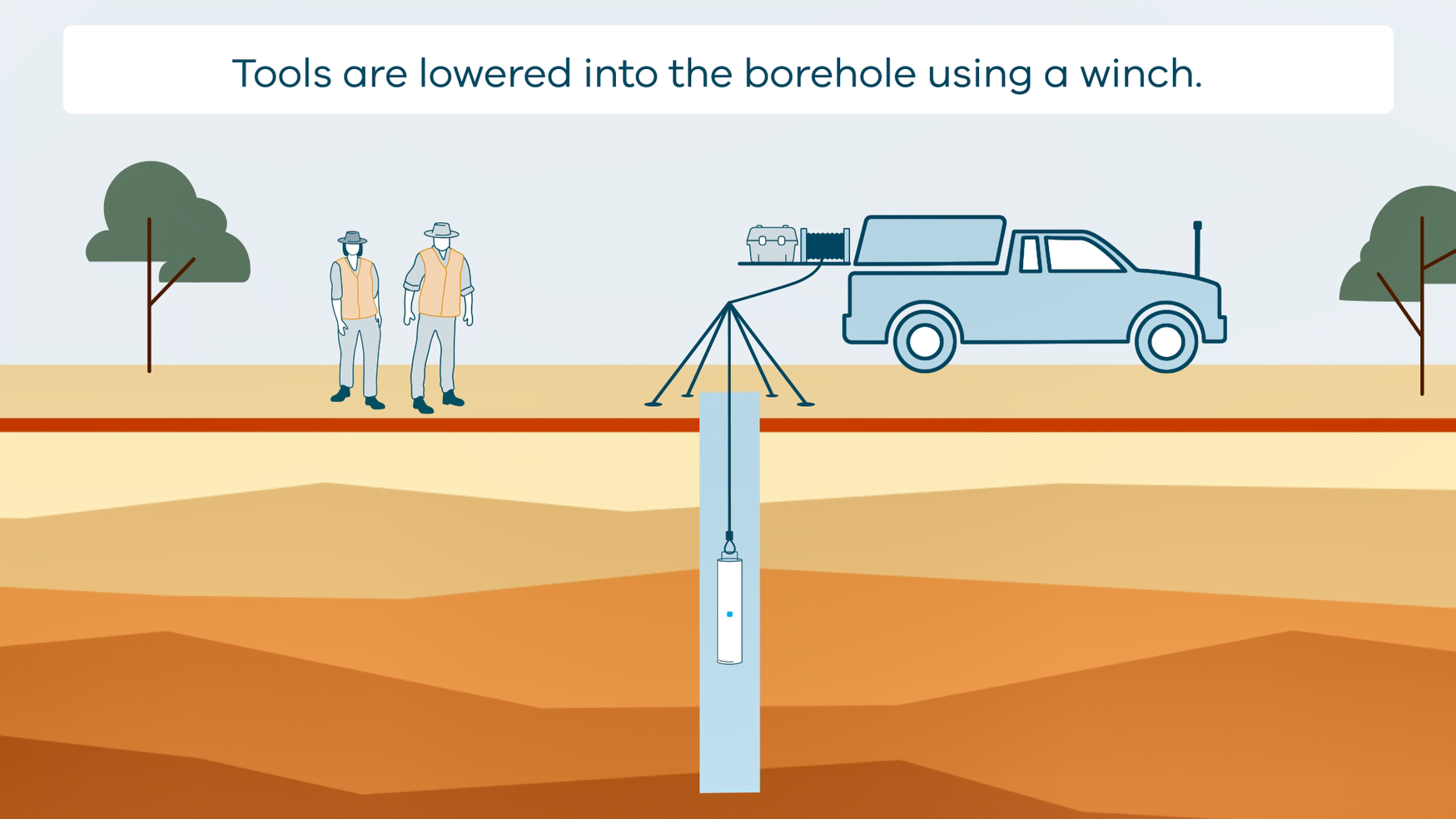
This animation shows how borehole geophysical surveys are conducted. It is part of a series of Field Activity Technique Engagement Animations. The target audience are the communities that are impacted by GA's data acquisition activities. There is no sound or voice over. The 2D animation includes a simplified view of what borehole geophysics equipment looks like, what the equipment measures and how scientists use the data.