dating
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Topics
-
This collection consists of type specimens, illustrated or referred specimens which have been published in the scientific literature. Type specimens that have been published in literature of a wide variety of different macro and micro fossils. The Commonwealth Palaeontological Collection is a collection of type, illustrated referred or cited specimens of fossils which have been published in the scientific literature. This Collection was initiated by Federal Cabinet decision during the 1920s. When fossil specimens of any new species of animal or plant are found, for it to be of any future use in biostratigraphy, it of course must be analysed.
-
Canning Basin Chart updated August 2013
-
The geological evolution of Australia is closely linked to supercontinent cycles that have characterised the tectonic evolution of Earth, with most geological and metallogenic events relating to the assembly and breakup of Vaalbara, Kenorland, Nuna, Rodinia and Pangea-Gondwana. Australia largely grew from west to east, with two major Archean cratons, the Yilgarn and Pilbara Cratons, forming the oldest part of the continent in the West Australian Element. The centre consists mostly of the largely Paleo-to Mesoproterozoic North and South Australian Elements, whereas the east is dominated by the Phanerozoic-Mesozoic Tasman Element. The West, North and South Australian Elements initially assembled during the Paleoproterozoic amalgamation of Nuna, and the Tasman Element formed as a Paleozoic accretionary margin during the assembly of Gondwana-Pangea. Australia's present position as a relatively stable continent resulted from the break-up of Gondwana. Australia is moving northward toward southeast Asia, probably during the earliest stages of the assembly of the next supercontinent, Amasia. Australia's resources, both mineral and energy, are linked to its tectonic evolution and the supercontinent cycle. Clusters of resources, both in space and time, are associated with Australia's tectonic history and the Earth's supercontinent cycles. Australia's most important gold province is the product of the assembly of Kenorland, whereas its major zinc-lead-silver deposits and iron-oxide-copper-gold deposits formed as Nuna broke up. The diverse metallogeny of the Tasman Element is a product of Pangea-Gondwana assembly and most of Australia's hydrocarbon resources are a consequence of the break-up of this supercontinent.
-
This report presents new geochronological results for five uranium deposits in Australia, detailing the timing of uranium mineralisation in relation to regional geological events. The purpose of the study is to better constrain ore genetic and exploration models for these uranium mineral systems, and ultimately to improve understanding of the uranium resource potential of the Australian continent. The work was carried out under the auspices of the Onshore Energy Security Program. Each of the five uranium deposits represents a different style of mineralisation within three broad families of uranium mineral systems: magmatic-related, basin-related, and metamorphic-related. The results contribute to the current paucity of age data for uranium deposits in Australia, and for most of the deposits the new dates are the first reported direct ages for mineralisation or associated alteration.
-
Northern Carnarvon Basin Biozonation and Stratrigraphy, 2008, Chart 34
-
Widespread reductions in the thickness and extent of Antarctic ice shelves are triggering retreat, acceleration and increased discharge of marine-terminating glaciers. However, while the impacts of recent ice-shelf changes are now well documented, their role in modulating past ice sheet dynamics – especially at a resolution required to identify drivers of change and test ice sheet models - remains poorly constrained. This reflects two persistent issues: (i) the effective discrimination between sediments and landforms deposited in a sub-ice-shelf setting from other glacimarine environments, and (ii) challenges associated with dating these records. Here we summarise recent progress in deciphering the ‘geological imprint’ of Antarctic ice shelves, including important advances in dating methods and the proxies required to reconstruct the drivers of change. Despite this improved ‘toolbox’ for establishing ice shelf presence and absence, we recognise several challenges that need to be overcome if we are to fully exploit the palaeo record. <b>Citation:</b> Smith, J.A., Graham, A.G.C., Post, A.L. et al. The marine geological imprint of Antarctic ice shelves. <i>Nat Commun</i> <b>10</b>, 5635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13496-5
-
Browse Basin Biozonation and Stratigraphy, 2008, revised February 2008
-
Bonaparte Basin biostratigraphic chart
-
The Lower Darling Valley (LDV) contains Cenozoic shallow marine, fluvial, lacustrine and aeolian sediments capped by a number of Quaternary fluvial units associated with the Darling River and its anabranches, which were poorly dated prior to this study. Recent investigations in the LDV area have used an Airborne Electromagnetic (AEM) survey, a new high-resolution LiDAR survey, sonic drilling, shallow hand-augering, examination of tractor-dug pits, sediment sample analyses, landform mapping, and river bottom profiling in combination with OSL and radiocarbon dating to provide new insights into the nature and chronology of Quaternary fluvial landscape evolution. The Quaternary sequence in the LDV consists of scroll-plain tracts of different ages incised into higher, older and more featureless floodplain sediments. Samples for OSL and radiocarbon dating were taken in tractor-excavated pits, from sonic cores and from hand-auger holes from a number of scroll-plain and older floodplain sediments. The youngest, now inactive, scroll-plain phase associated with the modern Darling River, was active in the period 5-2 ka. A previous anabranch scroll-plain phase has Last Glacial Maximum dates around 20 ka. Less distinct scroll-plain tracts, older than the anabranch system, have ages around 30ka. A poorly preserved scroll-plain phase with very indistinct scroll and channel traces is associated with the Darling River tract and has ages around 45-50 ka. Older dates of 85 ka and >150 ka have been obtained beneath the higher floodplain from lateral-migration sediments that lack visible scroll-plain traces. This chronologic sequence suggests regular recurrence of approximately 5 ka lateral-migration episodes separated by approximately 10 ka periods of quiescence. There is a lack of coincidence with the glacial-interglacial climate cycles. This suggests that the onset and termination of lateral-migration phases is probably a combination of changes in discharge and sediment regimes r
-
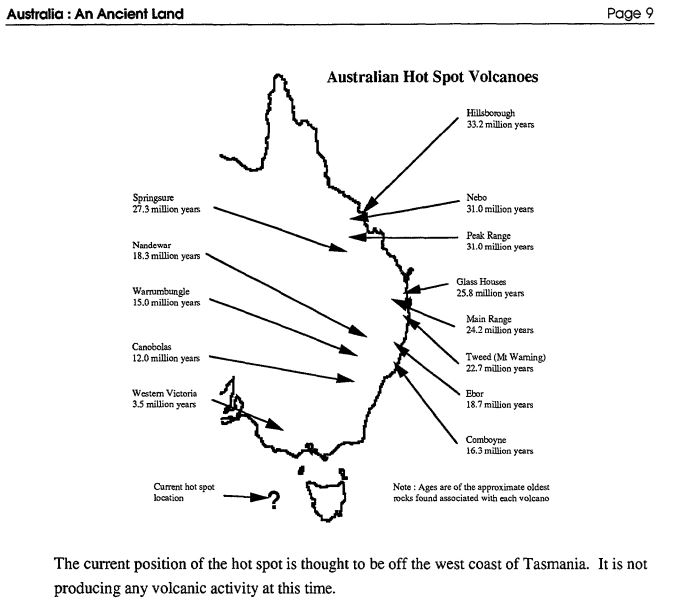
This black and white resource is an 18 page booklet including geological time, rock clocks, the age of famous Australian places, Australia on the move, Australian volcanoes, Ice Ages, Ancient Australian life, how fossils form and some common Australian fossils. Includes student activities suitable for primary Years K-6.