Education
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Scale
Topics
-
5 educational posters created for the Sapphire Coast Marine Discovery Centre in Eden on Geomorphology, Geology, Land Use and Type, and Seabed Habitats.
-
CAML is a five year International Program which will be undertaken as a major activity during the International Polar Year. This project will bring together all known data on Antarctic marine biodiversity and ocean change. The Antarctic Ocean is one of the most sensitive ecosystems in the world. Research undertaken via CAML will produce fascinating images of the Southern Ocean Geoscience Australia's Marine and Coastal Group is contributing expertise in sea floor mapping and sediment core collection to CAML. The Australian Government Antarctic Division is collecting oceanographic data, video footage and sediment cores through hot-water drill holes in the Amery Ice Shelf. The sediment cores are collected using a corer designed and built by Geoscience Australia, and are being analysed by scientists at Geoscience Australia to understand the environmental history beneath this ice shelf. This project has now produced four cores. The only other core ever obtained from beneath an extant ice shelf from under the Ross Ice Shelf in the early 1970s showed no signs of life. However, several Amery cores contain diatom-rich sediments, and one contains a succession of benthic faunas that indicate progressive colonisation of the sub-ice sea floor as ice retreated and currents began to seep nutrients and plankton into the sub-ice shelf cavity.
-
Second edition of the Australian Coasts booklet, aimed at secondary teachers and their students.
-
Spatial distribution of sponge species richness and its relationship with environmental variables are important for the informed monitoring of ecosystem health and marine environmental management and conservation within the Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve, in the Timor Sea region, northern Australia. However, the spatially continuous data of sponge species richness is not readily available, and the relationship is largely unknown. In this study, we modelled sponge species richness data of 77 samples using random forest (RF) and generalised linear model (glm) and their hybrid methods with geostatistical techniques (i.e. ordinary kriging (OK) and inverse distance weighting (IDW)) based on seabed biophysical variables. These methods are RF, RFOK, RFIDW, glm, glmok and glmidw that is a new hybrid method. We also examined effects of model averaging using four averaged methods (RFOKRFIDW, RFRFOKRFIDW, glmokglmidw and glmglmokglmidw) and the effects of various predictor sets on the accuracy of predictive models. Four feature selection methods, 1) averaged variable importance (AVI), 2) Boruta, 3) knowledge informed AVI (KIAVI) and 4) recursive feature selection (rfe), were used for RF; and four variable selection methods: 1) stepAIC, 2) dropterm, 3) anova and 4) RF, were employed to select glm predictive models. Predictive models were validated based on 10-fold cross validation. Finally the spatial distribution of sponge richness was predicted using the most accurate model and examined. The main findings are 1) the initial input predictors affect the status of important and unimportant variables; 2) AVI is not always reliable and KIAVI is recommended for selecting RF predictive model, 3) using Boruta can improve the accuracy in comparison with the full model, but it may lead to sub-optimal models; and features selected using rfe are not optimal and can be even misleading; 4) the accuracy of glm predictive model did not align with AIC, deviance explained (%) and deviance explained adjusted (%), suggesting that conventional model selection approaches for glm is unable to identify reliable predictive models; 5) joint application of RF and AIC is a useful model selection approach for developing glm predictive models; 6) the goodness of fit should not be used to assess glm predictive models; 7) the hybrid methods have significantly improved the predictive accuracy for both RF and glm; and the hybrid methods of RF and geostatistical methods are considerably more accurate and able to effectively model count data; and 8) the relationships of sponge species richness with the predictors are non-linear, and high sponge species richness is usually associated with hard seabed features. This study further confirms that: 1) the initial input predictors affect the model selection for RF; 2) the inclusion of highly correlated predictors could improve predictive accuracy, providing important guideline for pre-selecting predictors for RF; and 3) the effects of model averaging are method dependent or even data dependent. This study also provides important information for future monitoring design, particularly on the areas where the management and conservation of sponge gardens should be focused.
-
Australia - Evolution of a Continent: Palaeogeographic Atlas
-
Geoscience Australia acquires satellite imagery from a range of Earth observation satellites. This poster focuses on Australian States and Territories and various satellite applications.
-
This advanced earthquake location and magnitude classroom activity is based on real data from the 2004 earthquake off Banda Aceh on the Indonesian Island of Sumatra. Extension exercises and teacher answer provided.
-
Crystals are truly fascinating. Crystals are found almost anywhere - in the classroom,kitchen, bathroom, and in nature, in the rocks beneath your feet. Some people are impressed by their shapes, colours and natural beauty. Others are intrigued with theirchemical structure and study the science of Crystallography. Other people believe that crystals have "powers" and can influence moods. This booklet will help you and your students understand the science of crystals - explore the facts, and dispel the myths.
-
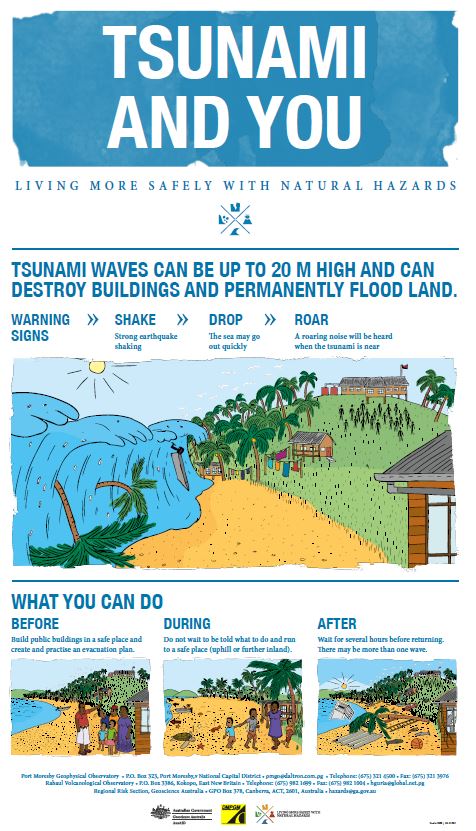
Educational booklet series on the hazards of East New Britain, Papua New Guinea: tsunamis, earthquakes & volcanoes
-
Geoscience Australia acquires satellite imagery daily, from a range of earth observation satellites, at our ground reception facilities at stations in Alice Springs and Hobart. The satellite image data vary in their spatial extent and resolution and have a range of applications. This poster provides some examples of the imagery provided by Geoscience Australia to a range of Government and other clients.
