Magnetism and palaeomagnetism
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Topics
-
<div>Geoscience Australia’s Exploring for the Future program provides precompetitive information to inform decision-making by government, community and industry on the sustainable development of Australia's mineral, energy and groundwater resources. By gathering, analysing and interpreting new and existing precompetitive geoscience data and knowledge, we are building a national picture of Australia’s geology and resource potential. This leads to a strong economy, resilient society and sustainable environment for the benefit of all Australians. This includes supporting Australia’s transition to net zero emissions, strong, sustainable resources and agriculture sectors, and economic opportunities and social benefits for Australia’s regional and remote communities. The Exploring for the Future program, which commenced in 2016, is an eight year, $225m investment by the Australian Government. This work contributes to building a better understanding of the Australian continent, whilst giving the Australian public the tools they need to help them make informed decisions in their areas of interest.</div><div><br></div><div>As part of the Australia's Resources Framework Project, in the Exploring for the Future Program, Geoscience Australia and CSIRO undertook a magnetic source depth study across four areas, with the objectives of generating cover model constraints from magnetic modelling to expand national coverage, and to improve our subsurface understanding of these areas. During this study, 2005 magnetic estimates of depth to the top of magnetization were generated, with solutions derived using a consistent methodology (targeted magnetic inversion modelling, or TMIM; also known as ‘sweet-spot’ modelling). The methodology for these estimates are detailed in a summary report by Foss et al (2024), and is available for download through Geoscience Australia’s enterprise catalogue (https://pid.geoscience.gov.au/dataset/ga/149239). </div><div><br></div><div>The new points were generated over four areas: 1) the western part of Tasmania that is the southernmost extension of the Darling-Curnamona-Delamerian (DCD) project area; 2) northeastern Queensland; 3) the Officer Basin area of western South Australia and southeastern West Australia; and 4) the Eastern Resources Corridor (ERC), covering eastern South Australia, southwest Queensland, western New South Wales and western Victoria. These depth estimates have been released, together with a summary report detailing the data and methodology used to generate the results, through Geoscience Australia's product catalogue (ecat) at https://pid.geoscience.gov.au/dataset/ga/149239.</div><div><br></div><div>This supplementary data release contains the chronostratigraphic attribution of the new TMIM magnetic depth estimates, which range in depth from at surface to 13,294 m below ground. To ensure that the interpretations took into account the local geological features, the magnetic depth estimates were integrated and interpreted with other geological and geophysical datasets, including borehole stratigraphic logs, potential fields images, surface and solid geology maps, and airborne electromagnetic interpretations (where available). </div><div><br></div><div>Each depth-solution is interpretively ascribed to either a chronostratigraphic boundary with the stratigraphic units above and below the depth estimate, or the stratigraphic unit that the depth estimate occurs within, populated from the Australian Stratigraphic Units Database (ASUD). Stratigraphic attribution adds value and informs users of the depth to certain stratigraphic units in their areas of interest. Each solution is accompanied by confidence estimates. The depth estimate points are formatted for compliance with Geoscience Australia’s (GA) Estimates of Geological and Geophysical Surfaces (EGGS) database, the national repository for standardised depth estimate points. </div><div><br></div><div>Results from these interpretations provided some support to stratigraphic drillhole targeting, as part of the Delamerian Margins NSW National Drilling Initiative campaign, a collaboration between GA’s EFTF program, the MinEx CRC National Drilling Initiative and the Geological Survey of New South Wales. The magnetic depth-estimate solutions produced within this study provide important depth constraints in data-poor areas. These data help to construct a better understanding of the 3D geometry of the Australian continent and aid in cover thickness modelling activities. The availability of the depth-estimate solutions via the EGGS database through Geoscience Australia’s Portal creates enduring value to the public.</div>
-
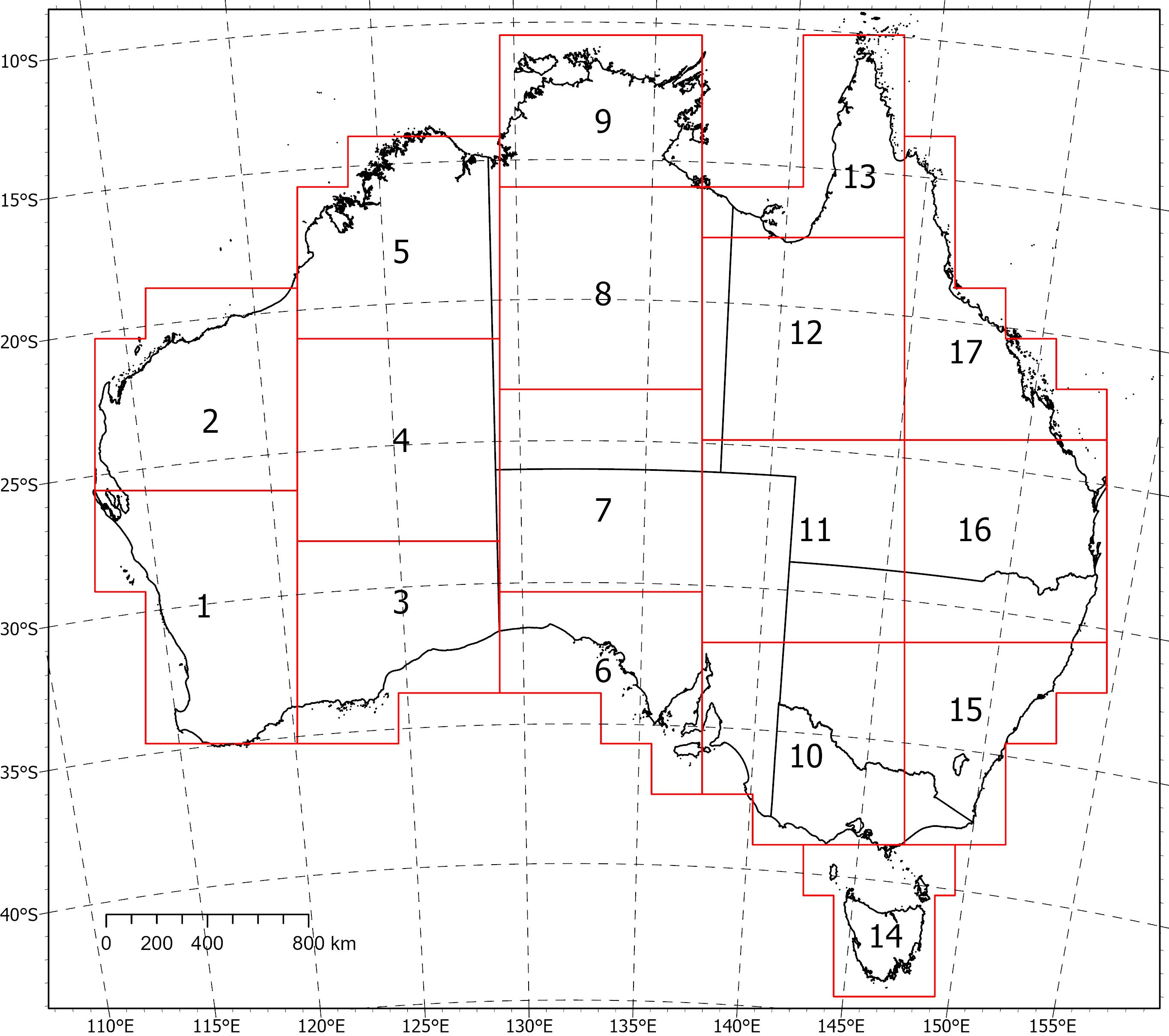
<div>Two coincident, crustal-scale models, one of magnetic susceptibility and one of density, have been produced for a volume covering the Australian continent and extending down to 55.5 km depth. These models were produced using the UBC‑GIF MAG3D and GRAV3D inversion programs, respectively.</div><div><br></div><div>The inversions were constrained with geological reference models with layers for sediments, undifferentiated crust and the mantle. The reference model for the magnetic inversion incorporated a Curie depth surface below which magnetic susceptibility was set to zero.</div><div><br></div><div>Due to the size of the inversion problem to be solved, the volume was divided into 235 overlapping inversions, which were inverted separately and then recombined. The method of recombining the inversions relies on a cosine function to determine the weight of each property and then takes a weighted average. This method successfully attenuated the edge effects that would otherwise occur between models and allows them to be viewed as one seamless model that covers the whole of Australia.</div><div><br></div><div>Regions of coincident high-density (>2.83 g/cm<sup>3</sup>) and high-magnetic susceptibility (>0.0125 SI) within the top 8‑9 km of the undifferentiated crust are suggested to be related to ultramafic rocks and the magnetite-forming hydrothermal alteration stages of potentially fertile IOCG systems. Currently the models are available in UBCGIF format (.den/.sus) only. Other formats and all supporting input data will be added in the near future. Due to their size, the models have been divided into subsets (labelled 1-17) for download. Please refer to the image below for the extent of the subsets.
-
<div>Near-surface magnetizations are ubiquitous across many areas of Australia and complicate reliable estimation of depth to deeper magnetizations. We have selected four test areas in which we use equivalent source dipoles to represent and quantify the near-surface magnetizations. We present a synthetic modelling study that demonstrates that field variations from the near-surface magnetizations substantially degrade estimation of depth to a magnetization 500 metres below the modelled sensor elevation and that these problems persist even for anomalies with significantly higher amplitudes. However, preferential attenuation of the fields from near surface magnetizations by upward continuation proved quite effective in improving estimation of depth to those magnetizations.</div> This Abstract was submitted/presented at the 2023 Australasian Exploration Geoscience Conference (AEGC) 13-18 March (https://2023.aegc.com.au/)
-
<div><strong>Purpose</strong></div><div>This package comprises a set of 86 thematic grids (rasters) derived from national coverages of gravity and magnetic survey data. These datasets provide valuable information about the distribution of geological features, physical property variations, and the composition of the Earth's crust. All grids have been resampled to the same cell size, map extent, and projection to allow them to be integrated into predictive mapping and modelling workflows using machine learning. Users can download individual grids or the whole grid package. </div><div> </div><div><strong>Input Data</strong></div><div>The following Australian national datasets were used:</div><div>1. 2019 Australian National Gravity Grids: Free Air Anomaly, Complete Bouguer Anomaly, De-trended Global Isostatic Residual, 400 m cell size (Lane <em>et al</em>., 2020).</div><div>2. Total Magnetic Intensity (TMI) Grid of Australia 2019 - seventh edition Enhanced Products Package (Morse, 2020).</div><div><br></div><div><strong>Processing</strong></div><div>All processing of the national grids were undertaken using Intrepid software. The following was performed on the input data:</div><div>1. The grids were reprojected from GDA94 geodetic to Australian Albers (EPSG 3577). </div><div>2. The grids were aligned to the same grid cell registration point and interpolated to fit within an 80 m cell size using a cubic spline method to ensure that the cell locations for all images are common.</div><div>3. Various Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT) were applied to each grid (see ‘Grids_for_Machine_Learning_dataset_notes.pdf’). </div><div> </div><div><strong>Metadata (all grids)</strong></div><div>· Datum: GDA94</div><div>· Projection: Australian Albers (EPSG 3577)</div><div>· Cell size: 80 m</div><div>· File format: GeoTiff (.tif)</div> <b>Data is available on request from clientservices@ga.gov.au - Quote eCat# 149130</b>
-
<div>As part of the Australia's Resources Framework Project, in the Exploring for the Future Program, Geoscience Australia and CSIRO have undertaken a magnetic source depth study across four areas. These are: 1) the western part of Tasmania that is the southernmost extension of the Darling-Curnamona-Delamerian (DCD) project area; 2) northeastern Queensland; 3) the Officer Basin area of western South Australia and southeastern West Australia; and 4) the 'Eastern Resources Corridor' (ERC) covering eastern South Australia, southwest Queensland, western New South Wales and western Victoria. This study has produced 2005 magnetic estimates of depth to the top of magnetization. The solutions are derived by a consistent methodology (targeted magnetic inversion modelling, or TMIM; also known as ‘sweet-spot’ modelling). </div><div><br></div><div>The magnetic depth estimates produced as part of this study provide depth constraints in data-poor areas. They help to construct a better understanding of the 3D geometry of the Australian continent, and aid cover thickness modelling activities. </div><div><br></div><div>A supplementary interpretation data release is also available through Geoscience Australia's enterprise catalogue (ecat) at https://pid.geoscience.gov.au/dataset/ga/149499.</div><div><br></div><div>Geoscience Australia’s Exploring for the Future program provides precompetitive information to inform decision-making by government, community and industry on the sustainable development of Australia's mineral, energy and groundwater resources. By gathering, analysing and interpreting new and existing precompetitive geoscience data and knowledge, we are building a national picture of Australia’s geology and resource potential. This leads to a strong economy, resilient society and sustainable environment for the benefit of all Australians. This includes supporting Australia’s transition to net zero emissions, strong, sustainable resources and agriculture sectors, and economic opportunities and social benefits for Australia’s regional and remote communities. The Exploring for the Future program, which commenced in 2016, is an eight year, $225m investment by the Australian Government. This work contributes to building a better understanding of the Australian continent, whilst giving the Australian public the tools they need to help them make informed decisions in their areas of interest.</div>
