GEOPHYSICS
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Topics
-
AusLAMP is a collaborative national project to cover Australia with long-period magnetotelluric (MT) data in an approximately 55 km spaced array. Signatures from past tectonothermal events can be retained in the lithosphere for hundreds of millions of years when these events deposit conductive mineralogy that is imaged by MT as electrically conductive pathways. MT also images regions of different bulk conductivity and can help to understand the continuation of crustal domains down into the mantle, and address questions on the tectonic evolution of Australia. The AusLAMP data presented here were collected as part of three separate collaborative projects involving several organisations. Geoscience Australia (GA), the Geological Survey of South Australia, the Geological Survey of New South Wales, the Geological Survey of Victoria, and the University of Adelaide all contributed staff and/or funding to collection of AusLAMP data; GA and AuScope contributed instrumentation. The data cover the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Curnamona Province, the Neoproterozoic Flinders Ranges, and the Cambrian Delamerian Orogen, encompassing eastern South Australia and western New South Wales and western Victoria. This project represents the first electrical resistivity model to image the entire Curnamona Province and most of the onshore extent of the Delamerian Orogen, crossing the geographical state borders between South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.
-
We present a resistivity model of the southern Tasmanides of southeastern Australia using Australian Lithospheric Architecture Magnetotelluric Project (AusLAMP) data. Modelled lower crustal conductivity anomalies resemble concentric geometries revealed in the upper crust by potential field and passive seismic data. These geometries are a key part of the crustal architecture predicted by the Lachlan Orocline model for the evolution of the southern Tasmanides, in which the Proterozoic Selwyn Block drives oroclinal rotation against the eastern Gondwana margin during the Silurian period. For the first time, we image these structures in three dimensions (3D) and show they persist below the Moho. These include a lower crustal conductor largely following the northern Selwyn Block margin. Spatial association between lower crustal conductors and both Paleozoic to Cenozoic mafic to intermediate alkaline volcanism and gold deposits suggests a genetic association i.e. fluid flow into the lower crust resulting in the deposition of conductive phases such as hydrogen, iron, sulphides and/or graphite. The 3D model resolves a different pattern of conductors in the lithospheric mantle, including northeast trending anomalies in the northern part of the model. Three of these conductors correspond to Cenozoic leucitite volcanoes along the Cosgrove mantle hotspot track which likely map the metasomatised mantle source region of these volcanoes. The northeasterly alignment of the conductors correlates with variations in the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) and the direction of Australian plate movement, and may be related to movement of an irregular LAB topography over the asthenosphere. By revealing the tectonic architecture of a Phanerozoic orogen and the overprint of more recent tectono-magmatic events, our resistivity model enhances our understanding of the lithospheric architecture and geodynamic processes in southeast Australia, demonstrating the ability of magnetotelluric data to image geological processes over time.
-
Geoscience Australia commissioned reprocessing of selected legacy 2D seismic data in the East Kimberley, onshore Bonaparte Basin as part of the Exploring for the Future (EFTF) program. Reprocessing of these data occurred between September 2017 and May 2018. Exploring for the Future (<a href="https://www.ga.gov.au/eftf/">https://www.ga.gov.au/eftf</a>) was a $100.5 million four-year (2016-20), Australian Government-funded program to provide a holistic picture of the potential mineral, energy and groundwater resources in northern Australia. The program has delivered new geoscience data, knowledge and decision support tools to support increased industry investment and sustainable economic development across the north. Groundwater is a critical resource that accounts for most water used across northern Australia. The groundwater component of the EFTF program focused on addressing groundwater resource knowledge gaps, to support future opportunities for economic development via irrigated agriculture, extractive industries and increased security of community water supplies. Through collaboration with State and Territory partners, the program undertook targeted regional investigations of groundwater systems and assessments of groundwater potential more broadly across the region. The program's activities, implemented by Geoscience Australia, involved application of innovative geoscience tools to collect, integrate and analyse a range of data. It includes geological and hydrogeological data, airborne and ground-based geophysical and hydrogeochemical surveys, remote sensing data as well as stratigraphic drilling. The new data and better understanding of groundwater systems also helps inform decision making about groundwater use to protect environmental and cultural assets. These outcomes strengthen investor confidence in resources and agricultural projects by de-risking groundwater in northern Australia. The package contains reprocessed data from ten surveys acquired between 1980 and 1997. In total 53 lines were reprocessed covering a fold area of approximately 618.9 line kilometres, with the objective to produce a modern industry standard 2D land seismic reflection dataset where possible from a selection of multiple legacy 2D data. The purpose of the reprocessing was twofold: 1) To image the near surface structural and stratigraphic configuration for linking to AEM data that is available in the Bonaparte Basin; and 2) To image the structure and stratigraphic architecture of the Paleozoic Bonaparte Basin. The dataset exhibits significant improvements in stack response in most of the reprocessed lines when final and legacy stacks were compared, especially in the shallow section. Optimum results were obtained from the noise attenuation workflows. A minimum processing flow was applied to BWA80, BWA81, and line BNT87-404 lines to avoid any signal leakage throughout the processing. Final data were delivered as minimum phase (care should be taken not to interpret zero crossings as geological boundaries), and final velocities produced a good match with the well checkshot velocities. The processing report from Down Under Geophysics is available for download with this release. Raw and processed data are available on request from <a href="mailto:clientservices@ga.gov.au&body=Ref: eCat 135578">clientservices@ga.gov.au</a> - Quote eCat# 135578. Processed stack SEG-Y files and ancillary data are available for download from this web page.
-
Geoscience Australia commissioned reprocessing of selected legacy onshore 2D reflection seismic data in the Kidson Sub-basin of the Canning Basin, Cobb Embayment in the SE Canning Basin, NW Canning Basin, and Southern Carnarvon, Western Australia. This reprocessing is a collaboration between the Geoscience Australia Exploring for the Future (EFTF) program and The Government of Western Australia, Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety, Exploration Incentive Scheme (EIS). Reprocessing was carried out by Ion (Cairo) between January 2018 and September 2018. The Canning project comprised 30 lines from 5 vintages of data totalling 1412 km. The Carnarvon project comprised 36 lines from 6 vintages of data totalling 1440 km. This reprocessing is intended to produce an improved quality seismic dataset that will increase confidence in the mapping of the structure and stratigraphy of the onshore sedimentary basins of Western Australia. The new seismic reprocessed data is being made available as pre-competitive information to assist industry to better target areas likely to contain the next major oil, gas and mineral deposits. <b>Processed data for this survey are available on request from clientservices@ga.gov.au - Quote eCat# 144258</b>
-
In association with the OB2020 seismic survey, over 8,200 line kilometre of gravity and magnetic data were acquired. These data were subsequently merged with existing satellite data to produce merged grids at 1000m grid cell size. Several enhancement processing techniques were applied to these magnetic and gravity data to better highlight buried features within the Otway Basin. The merged input data from the survey and the enhanced products in this release provide valuable information on the geometry and spatial extent of igneous rocks in the deep-water basin. The distribution of these rocks is critical to the understanding of the petroleum systems and therefore the hydrocarbon prospectivity of the area. This data package contains: 1) A metadata statement document 2) Shapefiles of the magnetic and gravity line data from the OBSP survey 3) ASCII xyz grids of the OBSP and merged grids with public domain data 4) Georeferenced (GeoTIFF) images of the survey and merged grids 5) Gravity and Magnetic data processing reports from the OBSP survey
-
The discovery of strategically located salt structures, which meet the requirements for geological storage of hydrogen, is crucial to meeting Australia’s ambitions to become a major hydrogen producer, user and exporter. The use of the AusAEM airborne electromagnetic (AEM) survey’s conductivity sections, integrated with multidisciplinary geoscientific datasets, provides an excellent tool for investigating the near-surface effects of salt-related structures, and contributes to assessment of their potential for underground geological hydrogen storage. Currently known salt in the Canning Basin includes the Mallowa and Minjoo salt units. The Mallowa Salt is 600-800 m thick over an area of 150 × 200 km, where it lies within the depth range prospective for hydrogen storage (500-1800 m below surface), whereas the underlying Minjoo Salt is generally less than 100 m thick within its much smaller prospective depth zone. The modelled AEM sections penetrate to ~500 m from the surface, however, the salt rarely reaches this level. We therefore investigate the shallow stratigraphy of the AEM sections for evidence of the presence of underlying salt or for the influence of salt movement evident by disruption of near-surface electrically conductive horizons. These horizons occur in several stratigraphic units, mainly of Carboniferous to Cretaceous age. Only a few examples of localised folding/faulting have been noted in the shallow conductive stratigraphy that have potentially formed above isolated salt domes. Distinct zones of disruption within the shallow conductive stratigraphy generally occur along the margins of the present-day salt depocentre, resulting from dissolution and movement of salt during several stages. This study demonstrates the potential AEM has to assist in mapping salt-related structures, with implications for geological storage of hydrogen. In addition, this study produces a regional near-surface multilayered chronostratigraphic interpretation, which contributes to constructing a 3D national geological architecture, in support of environmental management, hazard mapping and resource exploration. <b>Citation: </b>Connors K. A., Wong S. C. T., Vilhena J. F. M., Rees S. W. & Feitz A. J., 2022. Canning Basin AusAEM interpretation: multilayered chronostratigraphic mapping and investigating hydrogen storage potential. In: Czarnota, K (ed.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, https://dx.doi.org/10.26186/146376
-
As part of the Exploring For the Future program 2022 showcase, Geoscience Australia (GA) in collaboration with the Australian Institute of Geoscientists held an Airborne Electromagnetics (AEM) workshop in Perth on 11th August 2022. The workshop comprised the following: - An introduction to GA's 20 km spaced continent-wide AusAEM program, by Karol Czarnota - How the Western Australia government has successfully used 20 km spaced AEM data, by Klaus Gessner - An introduction to AEM, surveying, and quality control given by Yusen Ley-Cooper - An introduction to inverse theory presented by Anandaroop Ray - Hands-on AEM modeling and inversion using HiQGA.jl by Anandaroop Ray - Integrating geophysics and geology in subsurface interpretation, by Sebastian Wong - Avoiding the 10 most common pitfalls in AEM interpretation according to Neil Symington YouTube video from the workshop, as well as data and code to follow along with the videos can be found on GA's GitHub at <a href=https://github.com/GeoscienceAustralia/HiQGA.jl/tree/workshop><u>this link.</u></a>
-
Drilling in the Geoscience Australia Exploring for the Future East Tennant project was conducted as part of the MinEx CRC National Drilling Initiative. Ten stratigraphic boreholes were drilled for scientific purposes in the region around the Barkly Roadhouse in the Northern Territory. Where possible, the boreholes were comprehensively wireline logged to obtain petrophysical data on the cover and basement rocks to help improve knowledge and geophysical models of the region. Formation density data obtained by wireline logging were validated using laboratory-based bulk density data obtained by Archimedes method on diamond drill core samples at Geoscience Australia. Results of the validation show that wireline-logged formation density data and Archimedes wet bulk density data are in good general agreement in the first five boreholes drilled (NDIBK01, NDIBK02, NDIBK03, NDIBK04 and NDIBK05). Difficult drilling and some lost drilling equipment meant that boreholes NDIBK06, NDIBK07 and NDIBK09 could not be cased properly, or could not be re-entered, and thus formation density wireline logs could not be obtained in these holes. Boreholes NDIBK08 and NDIBK10 were wireline logged, however formation density results from these last two holes were problematic. Wireline formation density results for borehole NDIBK08 are shown to be too high due to miscalibration of the wireline formation density tool, and results from borehole NDIBK10 cannot be robustly assessed because of a lack of sufficient Archimedes bulk density data needed to provide statistical relevance and validate the wireline formation density data.
-
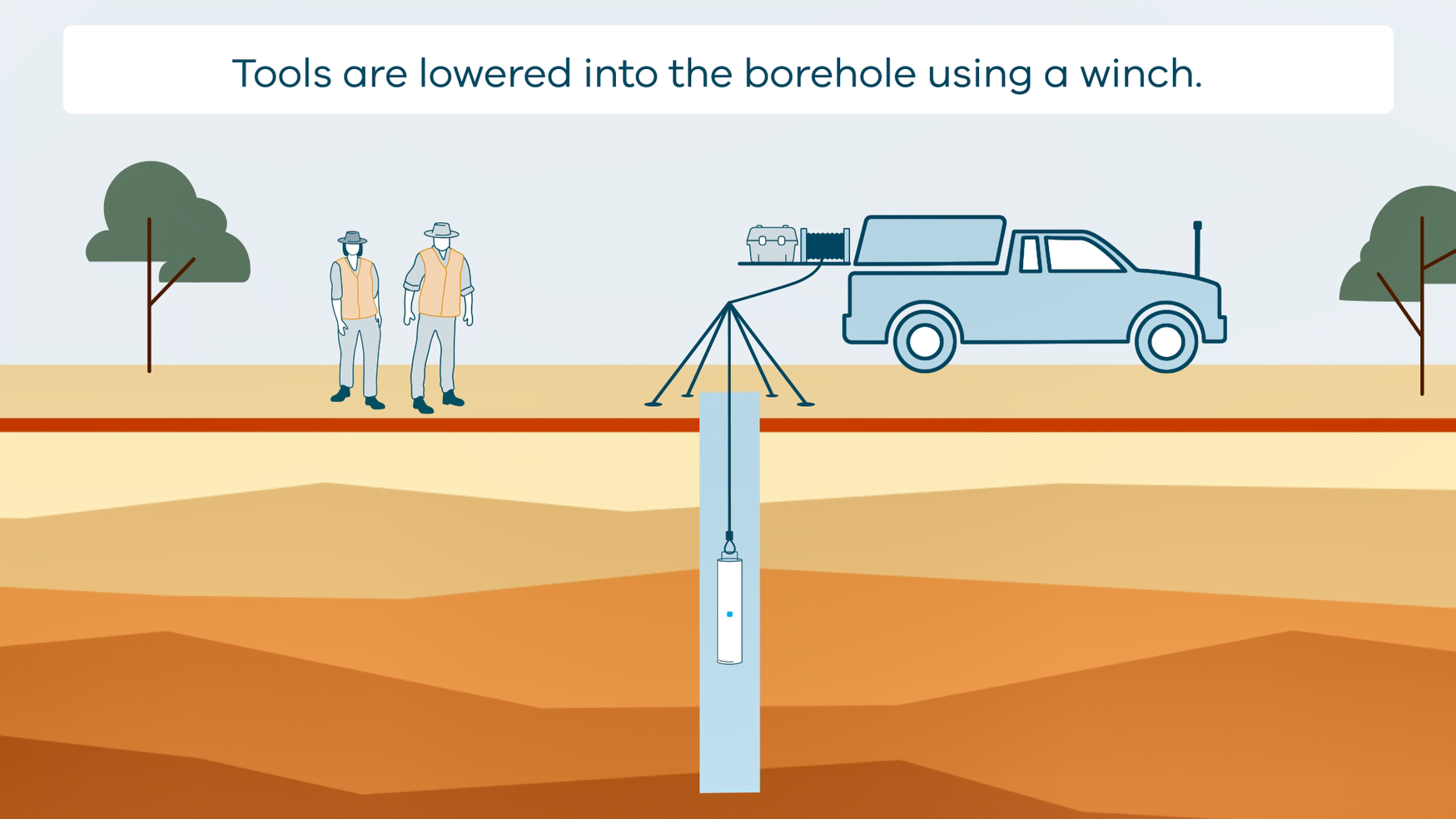
This animation shows how borehole geophysical surveys are conducted. It is part of a series of Field Activity Technique Engagement Animations. The target audience are the communities that are impacted by GA's data acquisition activities. There is no sound or voice over. The 2D animation includes a simplified view of what borehole geophysics equipment looks like, what the equipment measures and how scientists use the data.
-
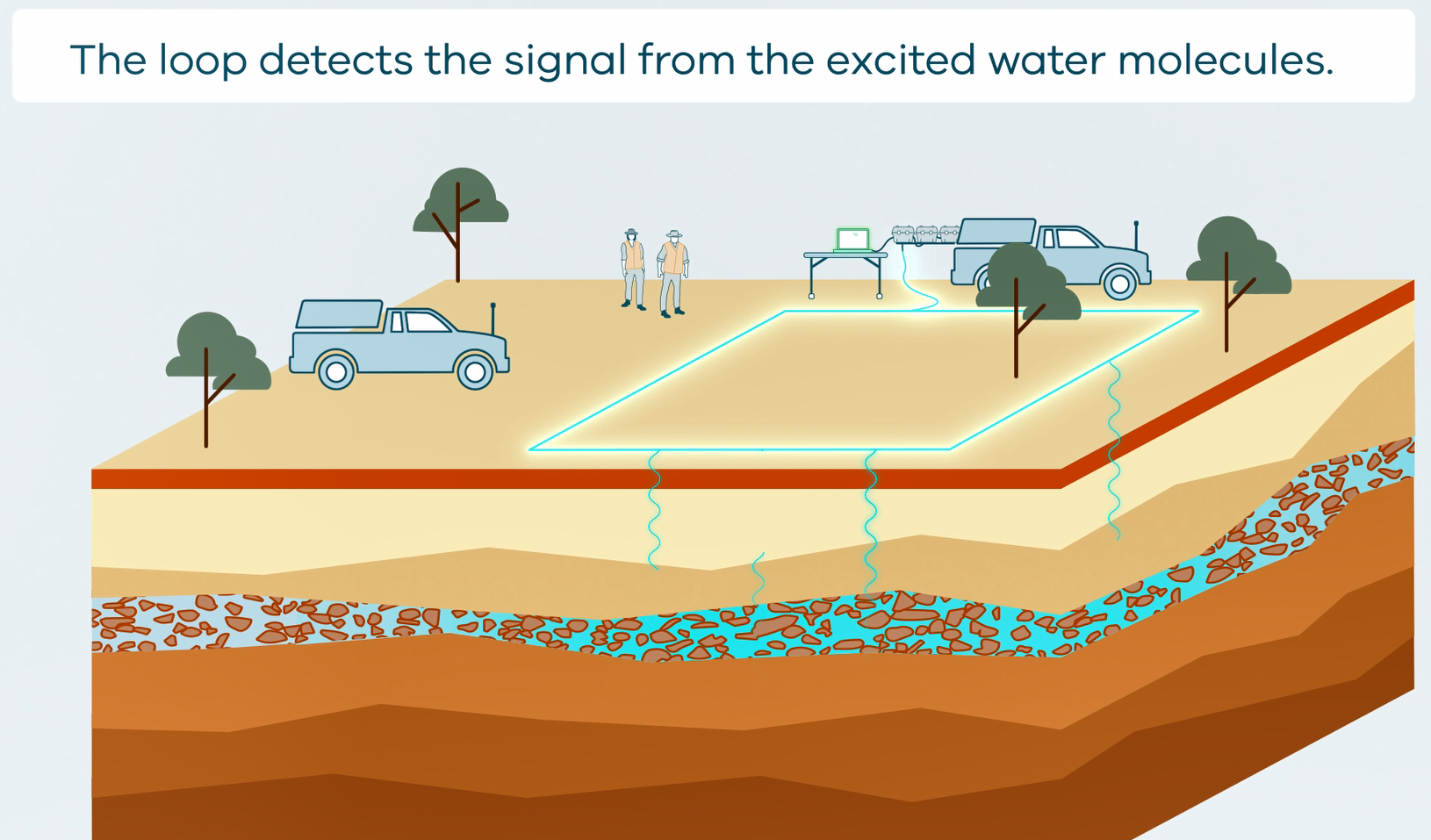
This animation shows how Surface Magnetic Resonance (SMR) Surveys are conducted. It is part of a series of Field Activity Technique Engagement Animations. The target audience are the communities that are impacted by GA's data acquisition activities. There is no sound or voice over. The 2D animation includes a simplified view of what SMR equipment looks like, what the equipment measures and how scientists use the data.