ENGINEERING
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Topics
-
Knowledge of the nature of buildings within CBD areas is fundamental to a broad range of decision making processes, including planning, emergency management and the mitigation of the impact of natural hazards. To support these activities, Geoscience Australia has developed a building information system called the National Exposure Information System (NEXIS) which provides information on buildings across Australia. Most of the building level information in NEXIS is statistically derived, but efforts are being made to include more detailed information on the nature of individual buildings, particularly in CBD areas. This is being achieved in Melbourne through field survey work.
-
Knowledge of the nature of buildings within business precincts is fundamental to a broad range of decision making processes, including planning, emergency management and the mitigation of the impact of natural hazards. To support these activities, Geoscience Australia has developed a building information system called the National Exposure Information System (NEXIS) which provides information on buildings across Australia. Most of the building level information in NEXIS is statistically derived, but efforts are being made to include more detailed information on the nature of individual buildings, particularly in business districts. This is being achieved in Adelaide through field survey work.
-
Knowledge of the nature of buildings within CBD areas is fundamental to a broad range of decision making processes, including planning, emergency management and the mitigation of the impact of natural hazards. To support these activities, Geoscience Australia has developed a building information system called the National Exposure Information System (NEXIS) which provides information on buildings across Australia. Most of the building level information in NEXIS is statistically derived, but efforts are being made to include more detailed information on the nature of individual buildings, particularly in CBD areas. This is being achieved in the Gold Coast through field survey work.
-
Knowledge of the nature of buildings within CBD areas is fundamental to a broad range of decision making processes, including planning, emergency management and the mitigation of the impact of natural hazards. To support these activities, Geoscience Australia has developed a building information system called the National Exposure Information System (NEXIS) which provides information on buildings across Australia. Most of the building level information in NEXIS is statistically derived, but efforts are being made to include more detailed information on the nature of individual buildings, particularly in CBD areas. This is being achieved in Hobart through field survey work.
-
The Girls in STEM statement addresses Strategy 2028 impact area of ‘enabling an informed Australia’ by increasing earth science literacy and engagement while addressing issues of diversity and inclusion. The Statement articulates Geoscience Australia’s efforts to engage girls in STEM, particularly as it relates to our education program.
-
<div>The region of coastal South East Queensland (SEQ) is a large concentration of population, industry, and infrastructure important to the economy of Queensland and of Australia. The region is also subject to severe storms that generate damaging winds, particularly as result of thunderstorm and tropical cyclone activity. Older residential housing has historically been the most damaged in such storms, contributing disproportionately to community risk. This risk posed by severe wind is not well understood, nor are the optimal strategies for managing, and potentially reducing, this risk. In this hazard context, this project was initiated based on a joint proposal developed by Queensland Fire and Emergency Services (QFES), Geoscience Australia and the six coastal local governments in SEQ in January 2020. The objective was to gain an improved understanding of the wind risks in this region and to develop actionable information that could inform future strategies to manage and reduce risk in these areas, with broader application to other local government areas. The project proved to be of great interest to a broader range of stakeholders, including the insurance industry, some of whom became formal partners, while others participated as observers. </div><div><br></div><div>The management of wind risk requires a sound evidence base for decision makers. While the information developed in this project has significant uncertainties, the outcomes are considered a representative view of wind risk in a coastal region that is home to nearly 60% of the Queensland population. The work has developed an improved understanding of the three primary risk elements of wind hazard, residential exposure and vulnerability. This has been achieved through a broad collaboration that has entailed the sharing of data, domain expertise and consensus building. This, in turn, has been translated into an assessment of scenario impacts, local scale risk, and the nuancing effects of resilience on the outcomes. An exploration was carried out of the effectiveness of a range of retrofit strategies directed at addressing the residential buildings in our communities that contribute the most wind risk in South East Queensland. The outcome are expected to be a valuable resource for all the project partners and stakeholders in the areas of planning, preparation, response, recovery and strategic mitigation.</div>
-
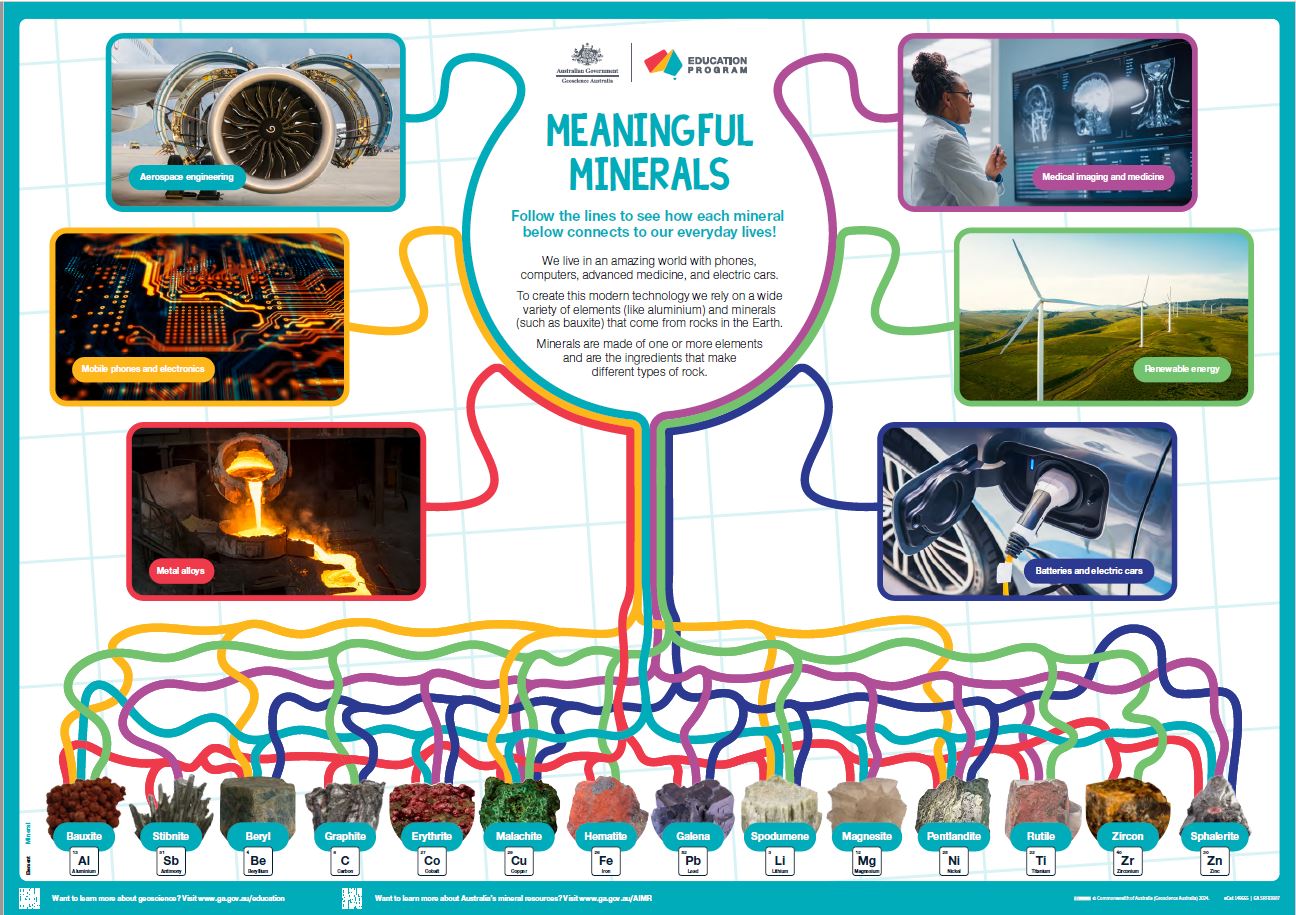
<div>This A1 poster aims to introduce Year 3/4 and older students to the many ways that minerals and elements are used in our everyday lives. </div><div> 6 key uses of 14 critical and strategic minerals are highlighted by colourful lines linking images. Students should take their time viewing the poster; they can follow the wiggly lines from minerals to product or vice versa and work out how many minerals link to each type of use.</div><div> The poster is also suitable for secondary students with the inclusion of a specific element name with each highlighted mineral plus the element symbol and atomic number.</div><div> The poster is intended to be a colourful rich stimulus to engage student interest in the resources from the ground used in our modern world.</div><div><br></div>
-
This brochure describes the work undertaken at Geoscience Australia (GA) to develop a blast loss estimation capability for the Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation. This brochure was developed to accompany a GA record on the same subject. (<a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.11636/Record.2016.022">eCat #101902</a>) Geoscience Australia has developed a modelling capability to estimate the potential impact of terrorist blasts in Australian central business districts (CBDs). With this information, the Australian Government is now able to more reliably estimate insured loss on behalf of the Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation (APRC). Insured loss is determined based on impact to buildings, contents and business interruption. This capability can now provide blast loss estimates to ARPC in a single business day for the Sydney, Melbourne, Adelaide and Brisbane CBDs. This capability is still in development for the Perth CBD and is expected to be operational by the end of 2016. This blast modelling capability allows ARPC to understand their financial exposure to a range of blast scenarios and assists them to ensure appropriate levels of reinsurance are held to respond to a terrorist incident. Should a terrorist incident occur, loss estimates can be continually reassessed as intelligence from the field is incorporated. Furthermore, the capability provides the ability to assess expected losses across CBDs through simulating many blast locations.
-
Knowledge of the nature of buildings within business precincts is fundamental to a broad range of decision making processes, including planning, emergency management and the mitigation of the impact of natural hazards. To support these activities, Geoscience Australia has developed a building information system called the National Exposure Information System (NEXIS) which provides information on buildings across Australia. Most of the building level information in NEXIS is statistically derived, but efforts are being made to include more detailed information on the nature of individual buildings, particularly in business districts. This is being achieved in Adelaide through field survey work.
-
This linked data API allows online access to all the AusPIX cells as a database. All DGGS cells, at all common resolutions, are mapped on individual landing pages, along with descriptors for spatial extent, centroid, neighbours, parent cells and child cells. Includes alternate views in a variety of formats, and can be manually or machine read. This is an online resource for the "AusPIX Data Integration by Locality Framework". It is built as a virtual database where the AusPIX DGGS Engine calculates information on demand. Location of this Linked data API is: https://fsdf.org.au/dataset/auspix/collections/auspix/items/R78523