Resource geoscience
Type of resources
Keywords
Publication year
Topics
-
<div>High purity quartz (HPQ) is the only naturally occurring and economically viable source for the production of silicon. Silicon is a critical mineral, and a key component in modern technologies such as semiconductors and photovoltaic cells. Critical minerals support the move towards a greater reliance on electrification, renewable energy sources and economic security. The global transition to net zero carbon emissions means there is a growing need for new discoveries of HPQ to supply the silicon production chain. High purity quartz deposits are identified in a multitude of geological settings, including pegmatites, hydrothermal veins, sedimentary accumulations and quartzite; however, deposits of sufficient volume and quality are rare. Quartz is abundant throughout Australia, but the exploration and discovery of HPQ occurrences is notably under-reported, making assessment of the HPQ potential in Australia extremely difficult. This paper presents a much-needed summary of the state of the HPQ industry, exploration and deposit styles in Australia. <b>Citation:</b> Jennings, A., Senior, A., Guerin, K., Main, P., & Walsh, J. (2024). A review of high-purity quartz for silicon production in Australia. <i>Australian Journal of Earth Sciences</i>, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2024.2362296
-
<div>Identifying potential basin areas for future Geological Storage of CO2 (GSC) exploration is essential to support Australia’s transition to a net zero emissions energy future. Geoscience Australia’s AFER Project has completed a play-based assessment of the GSC potential in the Pedirka and western Eromanga basins using regionally extensive aquifers containing saline to slightly brackish formation waters. There are currently no significant anthropogenic CO2 sources or associated storage projects in the assessment area. Understanding the area’s GSC potential does, however, assist in providing options for addressing CCS requirements in the central Australian region, including any future opportunities to remove anthropogenic CO2 using Direct Air Capture and Storage technologies. </div><div><br></div><div>The AFER Project’s assessments are underpinned by new geological insights into the basins and a supporting upscaled 3D geological model. A play-based common risk segment mapping approach has been applied to five potential storage (play) intervals to delineate basin areas with relatively high prospectivity based on four geological risk elements: injectivity, storage effectiveness, containment, and structural complexity. Results from this qualitative component of the assessment highlights a potentially prospective area for future GSC exploration extending across the Northern Territory, South Australia and Queensland. The most prospective interval on a geological probability of success basis is the Namur-Murta play interval. </div><div><br></div><div>Results from the qualitative GSC assessment have been used as a screening tool to delineate areas for quantitative modelling of the range of Estimated Ultimate Storage (EUS) volumes using deterministic and probabilistic methodologies. EUS volumes have been estimated in two model areas representing geological end members in storage interval heterogeneity and potentially prospective areas outside of the extents of current national parks. The EUS potential is high (10’s of gigatonnes) in the two model areas using both deterministic and probabilistic workflows, as expected for a regional assessment using very large pore volumes. Applying a geological probability of success based on injectivity and structural and stratigraphic containment reduces the volumes in the two model areas to a risked best estimate EUS of 13 Gt in the eastern area and a risked best estimate EUS of 2 Gt in the western area. Results from the quantitative assessment suggest that both model areas can support multiple industrial-scale CCS projects injecting 50 Mt CO2 over a 20-year period. However, heterogeneous reservoirs that extend over the eastern assessment area are likely to have greater storage efficiencies and an associated smaller project footprint of 29 km2 using three CO2 injection wells. Relatively homogenous reservoirs elsewhere in the assessment area have lower storage efficiencies due to a lack of intraformational seals within the Algebuckina Sandstone and have an associated larger project area of 49 km2 using three CO2 injection wells. Pressure management requirements are likely to be minimal in both model areas due to the thick and open nature of reservoirs. However, water production rates of up to 16,500 m3/day may be required where local lateral barriers to pressure dissipation occur. </div><div><br></div><div>Results from the AFER Project's GSC assessment demonstrate the value of applying a play-based exploration workflow for a regional-scale energy resource assessment. Estimating the geological probability of success to the presence and repeatability of four mappable risk elements associated with GSC resources allows both relative prospectivity maps and risked EUS volumes to be generated. Prospectivity maps and EUS volumes can in turn be readily updated as new geological data are collected to infill data and knowledge gaps. Geoscience Australia is building a national inventory of GSC resources using this play-based exploration approach, with qualitative assessments now completed under the EFTF and TEGI programs in seven basin areas from central and eastern Australia. </div><div><br></div>
-
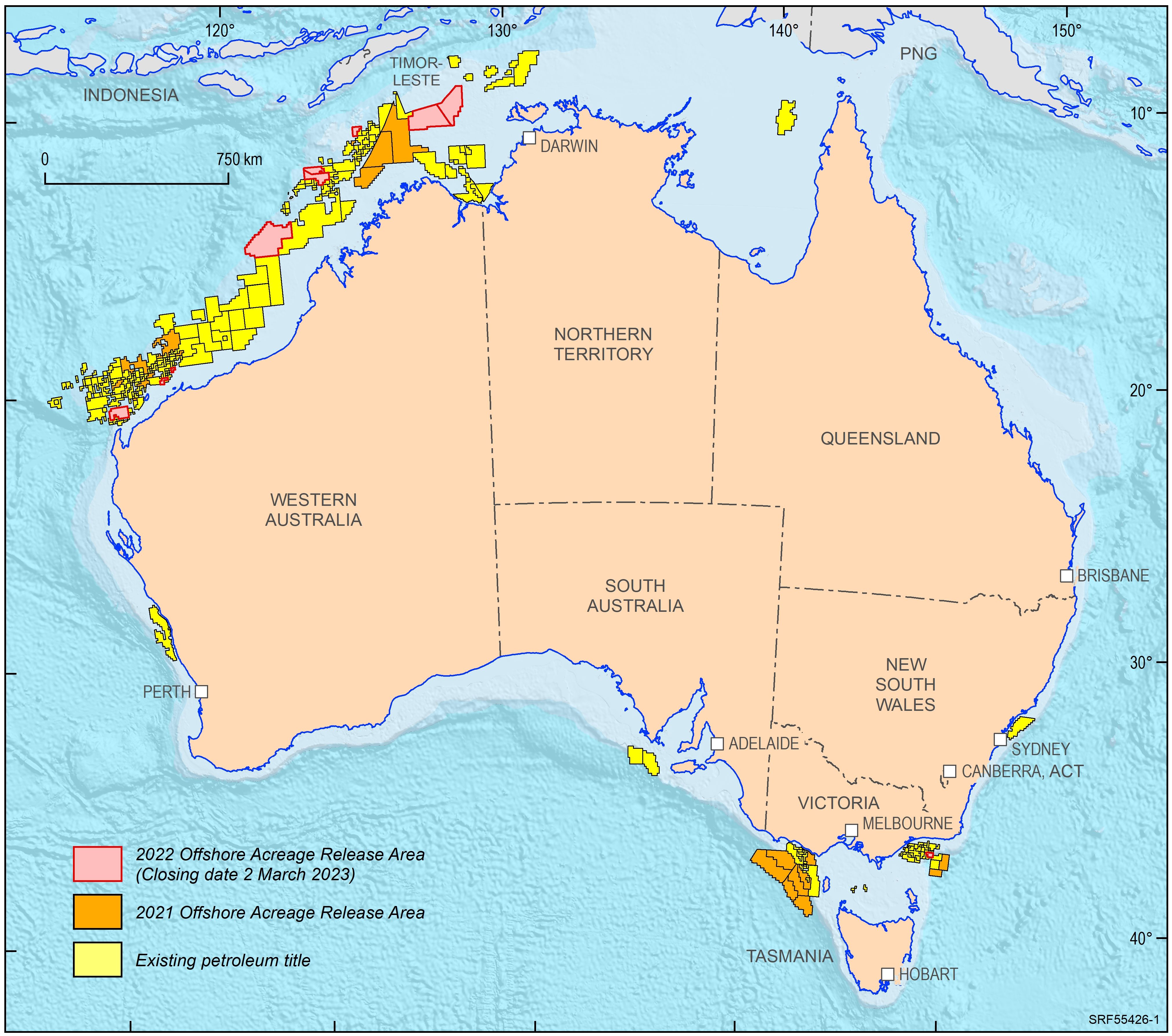
<div>In 2022, the Australian Government released ten offshore petroleum exploration areas. They are located in the Bonaparte Basin, Browse Basin, Northern Carnarvon Basin and Gippsland Basin. The areas highlight that producing provinces rather than data-poor regions are the preferred targets for exploration activities. In addition, the transition to low carbon energy resources, including opportunities for carbon capture and storage, has seen a diversification of energy companies’ portfolios. The Australian Government is supportive of the upstream energy industry, with natural gas seen as an important enabling energy resource commodity that supports the expansion of low emission technologies and related infrastructure. Most of the areas being offered for exploration in 2022 are likely to generate extra volumes of natural gas, both for domestic markets as well as securing feedstock for existing LNG export projects for the longer term. </div><div>Consistent with the approach of recent releases, only one period for work program bidding has been scheduled. The closing date for all bid submissions is 2 March 2023. </div><div>Geoscience Australia provides pre-competitive data and petroleum geological information in support of industry activities. Its petroleum geological studies aim to improve the understanding of the evolution of hydrocarbon-bearing basins at a regional scale and include a review of source rock and fluid occurrences, their geochemical characteristics, and petroleum systems modelling. Most recent examples include a sedimentological/stratigraphic study that investigates the depositional history of the southern Bonaparte Basin during the late Permian to Early Triassic evaluating the controls on reservoir facies development. A regional petroleum geological study of the Otway Basin, with a focus on the deeper water area and utilising newly industry acquired regional seismic data, provides new insights into the hydrocarbon prospectivity of this largely underexplored offshore part of the basin. Latest results of these studies were presented at this year’s APPEA conference. Large seismic and well data sets, submitted under the Offshore Petroleum and Greenhouse Gas Storage Act 2006 (OPGSSA) are made available through the National Offshore Petroleum Information Management System (NOPIMS). Additional data and petroleum related information can be accessed through Geoscience Australia’s data repository</div><div><br></div>
-
<div>NDI Carrara 1 is a 1750 m stratigraphic drill hole completed in 2020 as part of the MinEx CRC National Drilling Initiative (NDI) in collaboration with Geoscience Australia under the Exploring for the Future program and the Northern Territory Geological Survey. It is the first stratigraphic test of the Carrara Sub-basin, a recently discovered depocentre in the South Nicholson region. The drill hole intersected Cambrian and Proterozoic sediments consisting of organic-rich black shales and a thick sequence of interbedded black shales and silty sandstones with hydrocarbon shows. A comprehensive analytical program carried out by Geoscience Australia on the recovered core samples from 283 m to total depth at 1751 m provides critical data for calibration of burial and thermal history modelling.</div><div>Using data from this drilling campaign, burial and thermal history modelling was undertaken to provide an estimate of the time-temperature maxima that the sub-basin has experienced, contributing to an understanding of hydrocarbon maturity. Proxy kerogen kinetics are assessed to estimate the petroleum prospectivity of the sub-basin and attempt to understand the timing and nature of hydrocarbon generation. Combined, these newly modelled data provide insights into the resource potential of this frontier Proterozoic hydrocarbon province, delivering foundational data to support explorers across the eastern Northern Territory and northwest Queensland.</div> <b>Citation:</b> Palu Tehani J., Grosjean Emmanuelle, Wang Liuqi, Boreham Christopher J., Bailey Adam H. E. (2023) Thermal history of the Carrara Sub-basin: insights from modelling of the NDI Carrara 1 drill hole. <i>The APPEA Journal</i><b> 63</b>, S263-S268. https://doi.org/10.1071/AJ22048
-
<div><strong>Output Type: </strong>Exploring for the Future Extended Abstract</div><div><br></div><div><strong>Short Abstract: </strong>The continental crust directly hosts or underlies almost all mineral resources on which society depends. Despite its obvious importance its structure is poorly characterised. In particular, its density is surprisingly poorly constrained because it is difficult to directly image from the surface. Here we collate a global database of crustal thickness and velocity constraints. In combination with a compilation of published laboratory experimental constraints on seismic velocity at a range of pressures, we develop a scheme with which to convert seismic velocities into density as a function of pressure and temperature. We apply this approach to the Australian crystalline basement. We find that the Australian crust is highly heterogeneous, ranging in bulk density from 2.7—3.0 g cm-3. Finally, we explore the utility of our database for testing hypotheses about the location and endowment of mineral resources using porphyry copper deposits as an example. Our results provide an improved framework with which to explore the subsidence and thermal evolution of sedimentary basins, as well as probing relationships between deposit types and crustal architecture.</div><div><br></div><div><strong>Citation: </strong>Stephenson, S.N., Hoggard, M.J., Haynes, M.W., Czarnota, K. & Hejrani, B., 2024. Constraints on continental crustal thickness and density structure. In: Czarnota, K. (ed.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, https://doi.org/10.26186/149336</div>
-
<div>Geoscience Australia’s Exploring for the Future program provides precompetitive information to inform decision-making by government, community and industry on the sustainable development of Australia's mineral, energy and groundwater resources. Exploring for the Future program, which commenced in 2016, is an eight year, $225m investment by the Australian Government.</div><div><br></div><div>The Proterozoic Birrindudu Basin is an underexplored region that contains sparse geological data. Strata of similar age are highly prospective to the east, in the McArthur and South Nicholson basins and the Mount Isa region. To investigate this underexplored and data-poor region, the L214 Northwest Northern Territory Seismic Survey was acquired in August to September 2023 by GA and co-funded by the Northern Territory Government. Prior to this survey the region contained minimal seismic data. To complement the acquisition of the seismic survey, a sampling program of legacy stratigraphic and mineral exploration drill holes was also undertaken.</div><div><br></div><div>The new sampling program and seismic reflection data acquired over the Birrindudu Basin and its flanks, has identified many areas of exploration opportunity. This has almost tripled seismic coverage over the Birrindudu Basin, which has enabled new perspectives to be gained on its geology and relationship to surrounding regions. The new seismic has shown an increase in the extent of the Birrindudu Basin, revealing the presence of extensive concealed Birrindudu Basin sedimentary sequences and major, well preserved depocentres. In the central Birrindudu Basin and Tanami Region, shallow basement and deep-seated faults are encouraging for mineralisation, as these structures have the potential to focus mineralised fluids to the near surface. The clear presence of shallow Tanami Region rocks underlying the southern Birrindudu Basin sequences at the northern end of line 23GA-NT2 extends the mineral resource potential of the Tanami Region further north into the southern Birrindudu Basin. A new minimum age of 1822±7 Ma for the deposition of metasediments in drill hole LBD2 for rocks underlying the central Birrindudu Basin, extends the age-equivalent mineral-rich basement rocks of the Tanami Region north into the central Birrindudu Basin – extending the mineral resource potential into a new region.</div><div><br></div><div>The continuous stratigraphy imaged of the Birrindudu Basin by the new seismic is encouraging for energy prospectivity, as the system elements needed for an effective petroleum system, better defined by the new sampling program results, have been imaged to extend over a wider and deeper area. New organic petrological analysis and reflectance data indicate the sampled sections have reached thermal maturity suitable for hydrocarbon generation. Oil inclusion analyses provide evidence for oil generation and migration, and hence elements of a petroleum system are present in the central and northwestern Birrindudu Basin. With the expanded breadth of these rocks demonstrated on the seismic, this greatly increases the spatial extent of hydrocarbon prospectivity in Birrindudu Basin.</div>
-
<div><strong>Output type: </strong>Exploring for the Future Extended Abstract <strong> </strong></div><div><br></div><div><strong>Short abstract: </strong>There is an increased international focus on achieving high environmental, socio-economic, and governance (ESG) outcomes within mineral supply chains, in addition to delivering positive economic results. Mineral exploration and development projects must balance these disparate objectives to the satisfaction of separate stakeholders. However, the challenge of reconciling distinct preferences can obscure viable outcomes and confound project selection, particularly in the early stages of project development. Here, we discuss how such investment decisions can be treated as multicriteria optimization problems. In appraising the pre-competitive potential for nickel sulphide developments, we show how this approach can be used to effectively evaluate competing objectives and to locate regions that perform best under a range of different metrics. We outline a mapping framework that identifies Australian regions that optimally balance geological potential, economic value, and environmental impact. Our workflow creates a new capability within Australia to incorporate high-level, holistic information into the earliest stages of exploration. While this abstract focuses on mineral exploration, the modelling could be extended to other Australian resource development applications. Importantly, our results further underscore the need to compile baseline ESG datasets across Australia to help drive sustainable exploration decisions.</div><div><br></div><div><strong>Citation:</strong> Walsh S.D.C., Haynes M.W. & Wang C., 2024. Multicriteria resource potential mapping: balancing geological, economic & environmental factors. In: Czarnota, K. (ed.) Exploring for the Future: Extended Abstracts. Geoscience Australia, Canberra. https://doi.org/10.26186/149250</div>
-
<div>The Pedirka, Simpson and western Eromanga basins in central Australia have undergone a chequered exploration history which has seen a total of only 42 wells drilled across a study area of ~210,000km2. Exploration initially focused on conventional hydrocarbons from the 1950s-1980s, before shifting towards coal seam gas (CSG) opportunities in the mid-2000s. Active petroleum systems have been proven in the region by a non-commercial oil discovery at Poolowanna 1 in 1977, and by several wells that showed evidence of residual oil columns. CSG exploration wells have confirmed the presence of thick, marginally mature coal intervals on the flanks of the basins, but are yet to evaluate the deeper troughs.</div><div>Geoscience Australia, the Northern Territory Geological Survey and the South Australian Department for Energy and Mining have been collaborating on the Australia’s Future Energy Resources project under the Australian government funded Exploring for the Future Program to undertake an assessment of the resource potential for conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons, and the geological carbon and storage (GCS) potential of the greater Pedirka region. </div><div>The project applied a play-based exploration approach to qualitatively assess the resource potential of the region. The Carboniferous to Cretaceous stratigraphic interval was divided into 14 plays which were evaluated for the presence of sediment-hosted energy resources through post-drill analysis, gross depositional environment mapping and common risk segment mapping. The analysis identified energy resources and GCS potential across multiple plays and locations within the study area. These results demonstrate, that while the region is underexplored, it should not be overlooked by future exploration activities.</div> Published in The APPEA Journal 2023. <b>Citation:</b> Iwanec Jeremy, Strong Paul, Bernecker Tom (2023) Underexplored but not forgotten: assessing the energy resources potential of the greater Pedirka Basin region through play-based mapping. <i>The APPEA Journal</i><b> 63</b>, S251-S256. https://doi.org/10.1071/AJ22150
-
<div>Geoscience Australia and CSIRO have collaborated, under the Exploring for the Future program, to investigate whether water-saturated residual oil zones (ROZs), sometimes associated with conventional Australian hydrocarbon plays, could provide a CO2 storage resource and enhance the storage capacity of depleted fields. This product is part of a larger project that includes, among others, a petrophysical study to identify and characterise ROZs. </div><div>In this report, we model the formation of a residual oil zone in an Australian setting and the subsequent injection of CO2 using a 5 spot well pattern. The reservoir is built as an archetype example of the Hutton Formation from the Cooper-Eromanga basin. The reservoir interval is populated with "permeable sandstone” and “impermeable baffle” facies and a sealing layer at the top of the model is created and assigned properties such that it can be made to leak oil by capillary failure, as part of the process used to create a residual oil column. The static model is them imported into CMG-GEM software for the reservoir flow simulations. We find the scenario, with injectors perforated at the top and a central producing well perforated at the bottom, able to both store the most CO2 and produce the most oil. The storage and sweep efficiencies are high, highlighting the difference with typical CO2 storage scenarios without pressure mitigation.</div><div>For more information about this project and to access the related studies and products, see: https://www.eftf.ga.gov.au/carbon-co2-storage-residual-oil-zones. </div> <b>Data is available on request from clientservices@ga.gov.au - Quote eCat# 149366</b>
-
<div>Raster datasets of inferred magnesium number for the bulk lithospheric mantle across the Australian continent. The magnesium number is an elemental ratio, defined by Mg / (Mg + Fe), which correlates to the relative enrichment or depletion in incompatible elements. Oxide concentrations are inferred in from thermo-chemical inverse modelling of Rayleigh phase velocities, surface heat flow, geoid anomalies, and topography. The magnesium number rasters summarise the results of a Markov-chain Monte Carlo sampling of the posterior model space from an ensemble of plausible candidate models. Model release 'FR23' is developed using primary-mode Rayleigh phase velocity grids adapted from Fishwick & Rawlinson (2012; "3-D structure of the Australian lithosphere from evolving seismic datasets"). Model release 'KY22' is developed using the primary-mode Rayleigh phase velocity grids of Yoshizawa (2014; "Radially anisotropic 3-D shear wave structure of the Australian lithosphere and asthenosphere from multi-mode surface waves"). All models are products of the Exploring for the Future program.</div>